Abstract
The FK506-binding protein (FKBP12) is important in the immunosuppressant action of FK506 and rapamycin. We have investigated Trp side chain dynamics in FKBP12, with and without a bound immunosuppressant, by measuring the Trp time-resolved fluorescence anisotropy decay r(t). The r(t) for W59 in aqueous uncomplexed FKBP12 at 20 degrees C is well described by a single exponential with a recovered initial anisotropy, r(eff)o, of 0.192 and an overall rotational correlation time for the protein, phi p, of 4.7 ns; r(eff)o = 0.214 and phi p = 4.2 ns for the FKBP12/FK506 complex. Using an expression for the order parameter squared, namely S2 = r(eff)o/rTo, where rTo is the vitrified steady-state excitation anisotropy, we recovered an S2 of 0.75 for W59 fluorescence in uncomplexed FKBP12 and S2 approximately equal to 1 in the FKBP12/FK506 complex. Results obtained for the FKBP12/rapamycin complex are similar to those found for the FKBP12/FK506 complex. Minimum perturbation mapping simulations were performed on the free and complexed forms of FKBP12 and the results were generally in agreement with the experimental data.
Full text
PDF







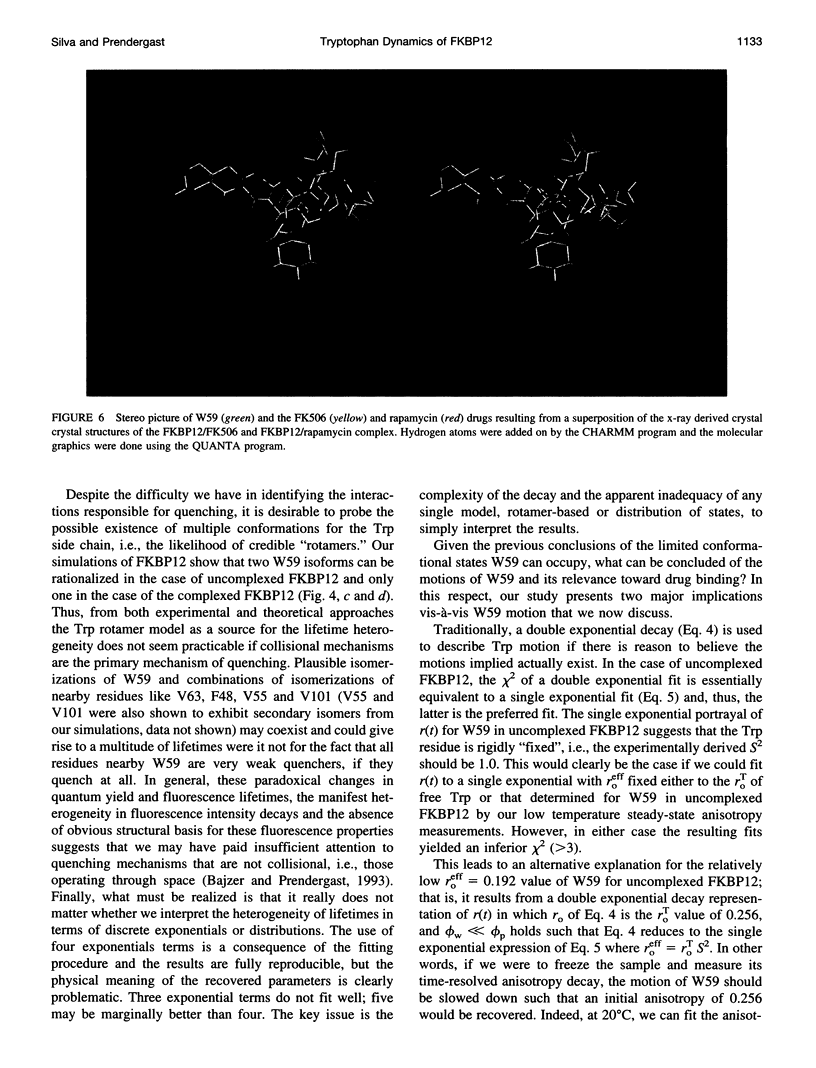




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcala J. R., Gratton E., Prendergast F. G. Interpretation of fluorescence decays in proteins using continuous lifetime distributions. Biophys J. 1987 Jun;51(6):925–936. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83420-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajzer Z., Prendergast F. G. A model for multiexponential tryptophan fluorescence intensity decay in proteins. Biophys J. 1993 Dec;65(6):2313–2323. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81325-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajzer Z., Zelić A., Prendergast F. G. Analytical approach to the recovery of short fluorescence lifetimes from fluorescence decay curves. Biophys J. 1995 Sep;69(3):1148–1161. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)79989-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker J. W., Rotonda J., McKeever B. M., Chan H. K., Marcy A. I., Wiederrecht G., Hermes J. D., Springer J. P. FK-506-binding protein: three-dimensional structure of the complex with the antagonist L-685,818. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11335–11339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beechem J. M., Brand L. Time-resolved fluorescence of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:43–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.000355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierer B. E., Mattila P. S., Standaert R. F., Herzenberg L. A., Burakoff S. J., Crabtree G., Schreiber S. L. Two distinct signal transmission pathways in T lymphocytes are inhibited by complexes formed between an immunophilin and either FK506 or rapamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9231–9235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J., Albers M. W., Shin T. B., Ichikawa K., Keith C. T., Lane W. S., Schreiber S. L. A mammalian protein targeted by G1-arresting rapamycin-receptor complex. Nature. 1994 Jun 30;369(6483):756–758. doi: 10.1038/369756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J. W., Lepre C. A., Chambers S. P., Fulghum J. R., Thomson J. A., Moore J. M. 15N NMR relaxation studies of the FK506 binding protein: backbone dynamics of the uncomplexed receptor. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 7;32(35):9000–9010. doi: 10.1021/bi00086a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J. W., Lepre C. A., Moore J. M. 15N NMR relaxation studies of the FK506 binding protein: dynamic effects of ligand binding and implications for calcineurin recognition. Biochemistry. 1994 Apr 12;33(14):4093–4100. doi: 10.1021/bi00180a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clipstone N. A., Crabtree G. R. Identification of calcineurin as a key signalling enzyme in T-lymphocyte activation. Nature. 1992 Jun 25;357(6380):695–697. doi: 10.1038/357695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan D. A., Logan T. M., Liang H., Matayoshi E., Fesik S. W., Holzman T. F. Equilibrium denaturation of recombinant human FK binding protein in urea. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 2;32(8):1920–1927. doi: 10.1021/bi00059a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer S., Michnick S., Karplus M. A mechanism for rotamase catalysis by the FK506 binding protein (FKBP). Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 21;32(50):13830–13837. doi: 10.1021/bi00213a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frauenfelder H., Parak F., Young R. D. Conformational substates in proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:451–479. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frauenfelder H., Sligar S. G., Wolynes P. G. The energy landscapes and motions of proteins. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1598–1603. doi: 10.1126/science.1749933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. P., Kim J. L., Kim E. E., Sintchak M. D., Thomson J. A., Fitzgibbon M. J., Fleming M. A., Caron P. R., Hsiao K., Navia M. A. X-ray structure of calcineurin inhibited by the immunophilin-immunosuppressant FKBP12-FK506 complex. Cell. 1995 Aug 11;82(3):507–522. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90439-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding M. W., Galat A., Uehling D. E., Schreiber S. L. A receptor for the immunosuppressant FK506 is a cis-trans peptidyl-prolyl isomerase. Nature. 1989 Oct 26;341(6244):758–760. doi: 10.1038/341758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. L., Hudson B. S. Photophysics of tryptophan in bacteriophage T4 lysozymes. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 5;29(22):5276–5285. doi: 10.1021/bi00474a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison R. K., Stein R. L. Substrate specificities of the peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerase activities of cyclophilin and FK-506 binding protein: evidence for the existence of a family of distinct enzymes. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 24;29(16):3813–3816. doi: 10.1021/bi00468a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutnik C. M., Szabo A. G. Confirmation that multiexponential fluorescence decay behavior of holoazurin originates from conformational heterogeneity. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3923–3934. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janes S. M., Holtom G., Ascenzi P., Brunori M., Hochstrasser R. M. Fluorescence and energy transfer of tryptophans in Aplysia myoglobin. Biophys J. 1987 Apr;51(4):653–660. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83390-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemple M. D., Yuan P., Nollet K. E., Fuchs J. A., Silva N., Prendergast F. G. 13C NMR and fluorescence analysis of tryptophan dynamics in wild-type and two single-Trp variants of Escherichia coli thioredoxin. Biophys J. 1994 Jun;66(6):2111–2126. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)81006-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz J. R., Maliwal B. P., Cherek H., Balter A. Rotational freedom of tryptophan residues in proteins and peptides. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):1741–1752. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Farmer J. D., Jr, Lane W. S., Friedman J., Weissman I., Schreiber S. L. Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporin A and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90124-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquis-Omer D., Sanyal G., Volkin D. B., Marcy A. I., Chan H. K., Ryan J. A., Middaugh C. R. Stabilization of the FK506 binding protein by ligand binding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 16;179(2):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91879-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michnick S. W., Rosen M. K., Wandless T. J., Karplus M., Schreiber S. L. Solution structure of FKBP, a rotamase enzyme and receptor for FK506 and rapamycin. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):836–839. doi: 10.1126/science.1709301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. M., Peattie D. A., Fitzgibbon M. J., Thomson J. A. Solution structure of the major binding protein for the immunosuppressant FK506. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):248–250. doi: 10.1038/351248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro I., Pecht I., Stryer L. Subnanosecond motions of tryptophan residues in proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):56–60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco M., Tirado-Rives J., Jorgensen W. L. Mechanism for the rotamase activity of FK506 binding protein from molecular dynamics simulations. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 30;32(47):12864–12874. doi: 10.1021/bi00210a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park S. T., Aldape R. A., Futer O., DeCenzo M. T., Livingston D. J. PPIase catalysis by human FK506-binding protein proceeds through a conformational twist mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3316–3324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen B. F., Stock A. M., Ringe D., Petsko G. A. Crystalline ribonuclease A loses function below the dynamical transition at 220 K. Nature. 1992 Jun 4;357(6377):423–424. doi: 10.1038/357423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schevitz R. W., Bach N. J., Carlson D. G., Chirgadze N. Y., Clawson D. K., Dillard R. D., Draheim S. E., Hartley L. W., Jones N. D., Mihelich E. D. Structure-based design of the first potent and selective inhibitor of human non-pancreatic secretory phospholipase A2. Nat Struct Biol. 1995 Jun;2(6):458–465. doi: 10.1038/nsb0695-458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. L., Crabtree G. R. The mechanism of action of cyclosporin A and FK506. Immunol Today. 1992 Apr;13(4):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90111-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. L. Immunophilin-sensitive protein phosphatase action in cell signaling pathways. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):365–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J. J., Hung S. H., Poe M., Lin C. S., Sigal N. H. A cytosolic binding protein for the immunosuppressant FK506 has peptidyl-prolyl isomerase activity but is distinct from cyclophilin. Nature. 1989 Oct 26;341(6244):755–757. doi: 10.1038/341755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal N. H., Dumont F. J. Cyclosporin A, FK-506, and rapamycin: pharmacologic probes of lymphocyte signal transduction. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:519–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E. FK 506 versus cyclosporine. Transplant Proc. 1993 Feb;25(1 Pt 1):511–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Fung J., Jordan M., Shapiro R., Tzakis A., McCauley J., Johnston J., Iwaki Y., Jain A., Alessiani M. Kidney transplantation under FK 506. JAMA. 1990 Jul 4;264(1):63–67. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner R. F., Kirby E. P. The interaction of the ground and excited states of indole derivatives with electron scavengers. J Phys Chem. 1969 Dec;73(12):4130–4135. doi: 10.1021/j100846a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. W. FK-506--how much potential? Immunol Today. 1989 Jan;10(1):6–9. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valeur B., Weber G. Resolution of the fluorescence excitation spectrum of indole into the 1La and 1Lb excitation bands. Photochem Photobiol. 1977 May;25(5):441–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1977.tb09168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Duyne G. D., Standaert R. F., Karplus P. A., Schreiber S. L., Clardy J. Atomic structure of FKBP-FK506, an immunophilin-immunosuppressant complex. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):839–842. doi: 10.1126/science.1709302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verlinde C. L., Dijkstra B. W. Drug or tool, design or serendipity? Nat Struct Biol. 1995 Jun;2(6):429–432. doi: 10.1038/nsb0695-429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederrecht G., Hung S., Chan H. K., Marcy A., Martin M., Calaycay J., Boulton D., Sigal N., Kincaid R. L., Siekierka J. J. Characterization of high molecular weight FK-506 binding activities reveals a novel FK-506-binding protein as well as a protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21753–21760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. P., Yamashita M. M., Sintchak M. D., Rotstein S. H., Murcko M. A., Boger J., Thomson J. A., Fitzgibbon M. J., Black J. R., Navia M. A. Comparative X-ray structures of the major binding protein for the immunosuppressant FK506 (tacrolimus) in unliganded form and in complex with FK506 and rapamycin. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1995 Jul 1;51(Pt 4):511–521. doi: 10.1107/S0907444994014514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu N. T. Raman spectroscopy: a conformational probe in biochemistry. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1977;4(3):229–280. doi: 10.3109/10409237709102559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]