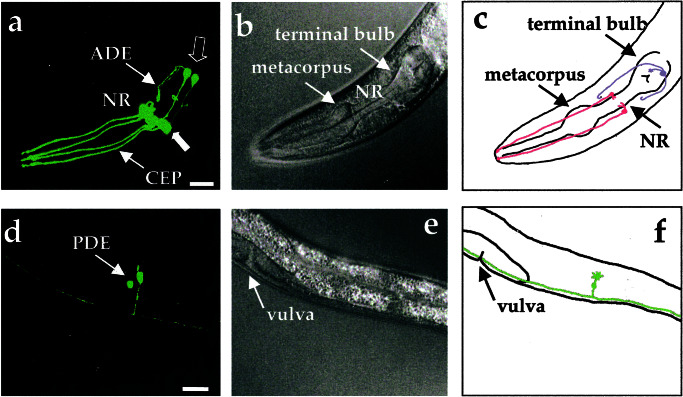
Figure 1.
Visualization of all eight dopamine neurons in living, adult C. elegans hermaphrodites by using DAT-1∷GFP transcriptional fusions. (a) Three-dimensional reconstruction of confocal epifluorescence from head dopamine neurons in a Pdat-1∷GFP transgenic line (BY200). Thin arrows identify CEP and ADE processes. Thick closed arrow points to four CEP cell bodies. Thick open arrow indicates location of two ADE cell bodies. NR refers to the nerve ring. (b) Differential interference contrast microscopy image of animal in a. (c) Schematic drawing showing location of dopamine neurons in the head relative to the pharynx. In this top view two pairs of CEP neurons (red) project dendritic endings to the tip of the nose and one pair of ADE neurons (blue) extend ciliated processes to amphids adjacent to the terminal bulb of the pharynx. (d) Three-dimensional reconstructions of confocal epifluorescence of the PDE neurons. Both PDE cell bodies are apparent. (e) Differential interference contrast microscopy image of animal in d. (f) Schematic drawing showing left-hand member of pair of PDE neurons (green) in lateral location posterior to vulva. (All scale bars = 25 μm.) Anterior is to the left.