Figure 4.
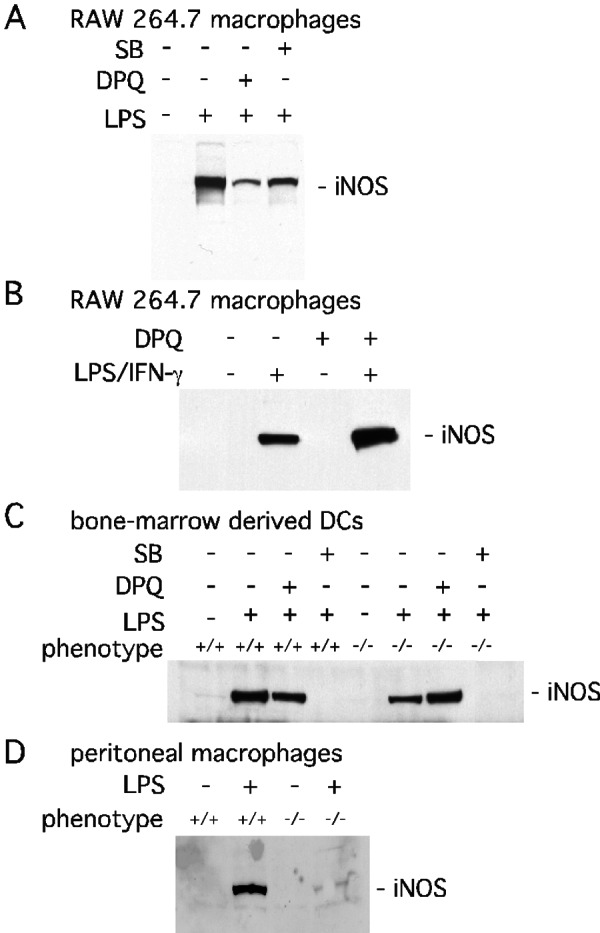
PARP-1 mediated iNOS expression is stimulus- and cell type-specific. (A) PARP activity-dependent iNOS expression induced by LPS. Treatment with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 24 h induced iNOS expression in RAW264.7 macrophages. LPS-induced iNOS expression was reduced substantially by DPQ (10 μM) and modestly by SB203580 (SB, 20 μM). (B) PARP activity-independent expression iNOS-induced by LPS/IFN-γ in RAW264.7 macrophages. DPQ (20 μM) increased iNOS expression after 24 h of treatment with LPS (1 μg/ml) and IFN-γ (400 units/ml). (C) PARP activity-independent iNOS expression in the primary DCs. LPS (1 μg/ml) for 24 h stimulated iNOS in PARP-1−/− cells but less than PARP-1+/+ cells. SB203580 (20 μM) abolished LPS-stimulated expression of iNOS in both PARP-1+/+ and PARP-1−/− cells. (D) Expression of iNOS in primary peritoneal macrophages. LPS-stimulated (1 μg/ml) expression of iNOS was attenuated significantly in PARP-1−/− peritoneal macrophages. Expression of iNOS was visualized by immunoblot with 100 μg of total protein from cells.
