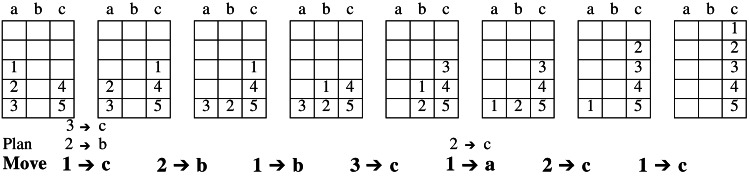
Figure 1.
Illustrative three-disk subproblem with plans and move by problem state. In this example, the initial configuration has disks 1, 2, and 3 in column a and disks 4 and 5 in column c. The goal state is to build a tower of all five disks in column c. The intermediate states shown here are the problem states in the optimal solution path, as determined by the strategy with which participants were trained. The plan and eventual move for each transition are shown below the corresponding problem states in the solution path. The succinct description of the strategy with which subjects were trained is described as follows: (i) Select the largest out-of-place disk and the destination peg. (ii) If there is no disk blocking the move, make the move and go to step i. (iii) If the largest disk blocking the move is on the destination, select it and the other peg and go to step ii. (iv) If the largest disk blocking the move is on the source, select it and the other peg and go to step ii. For example, the first move in this problem requires three planning steps resulting in the actual move of disk 1 to column c (actual moves are indicated in boldface). Each problem solved in the scanner was designed to include two of this type of three-disk subproblems. These subproblems are the focus of all analyses reported.