Abstract
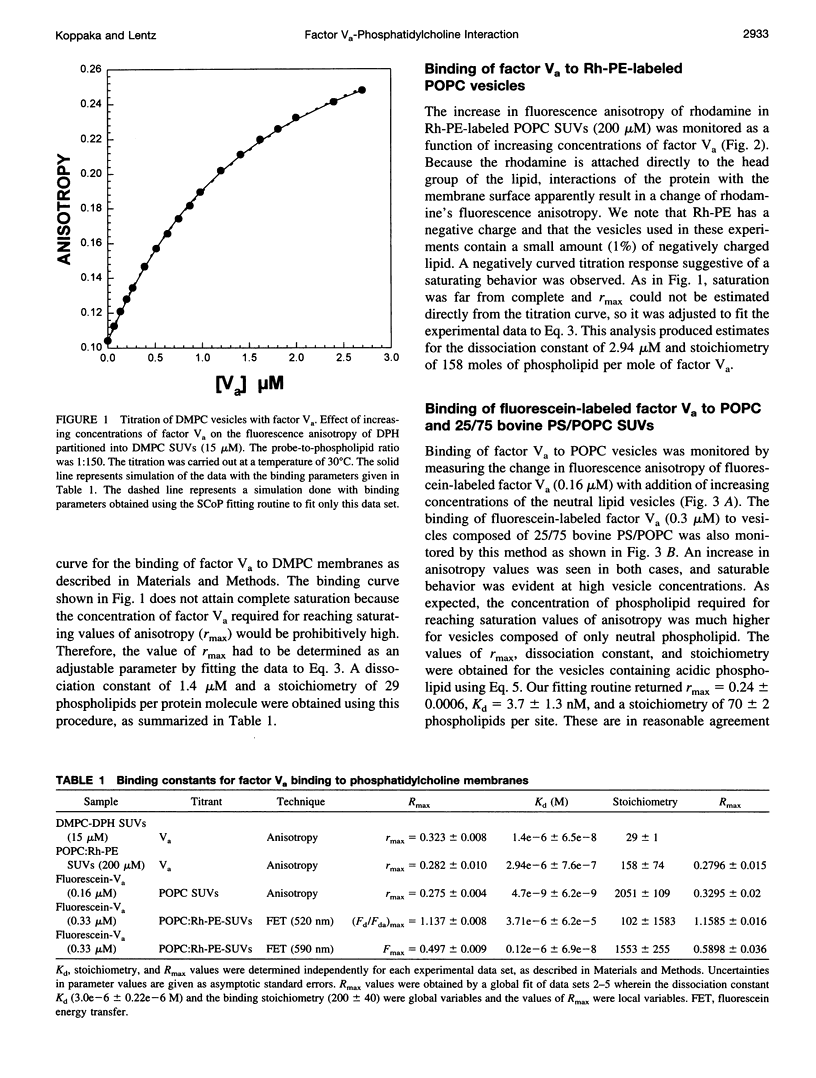
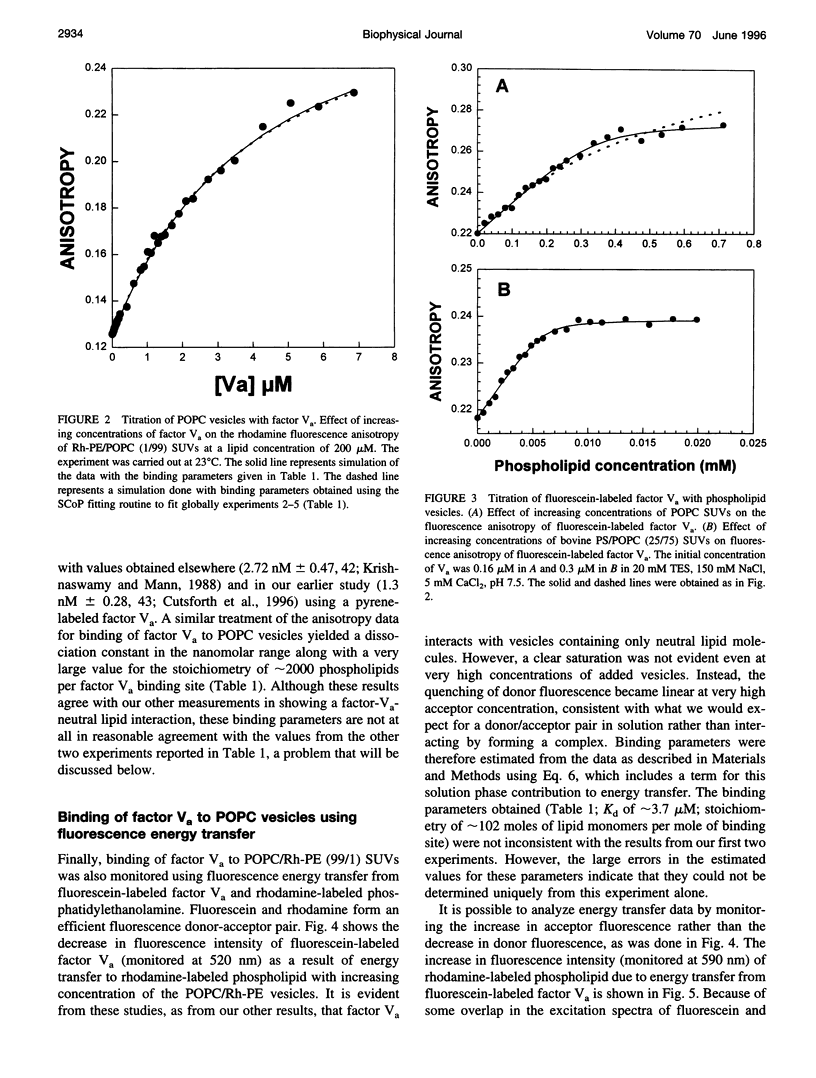
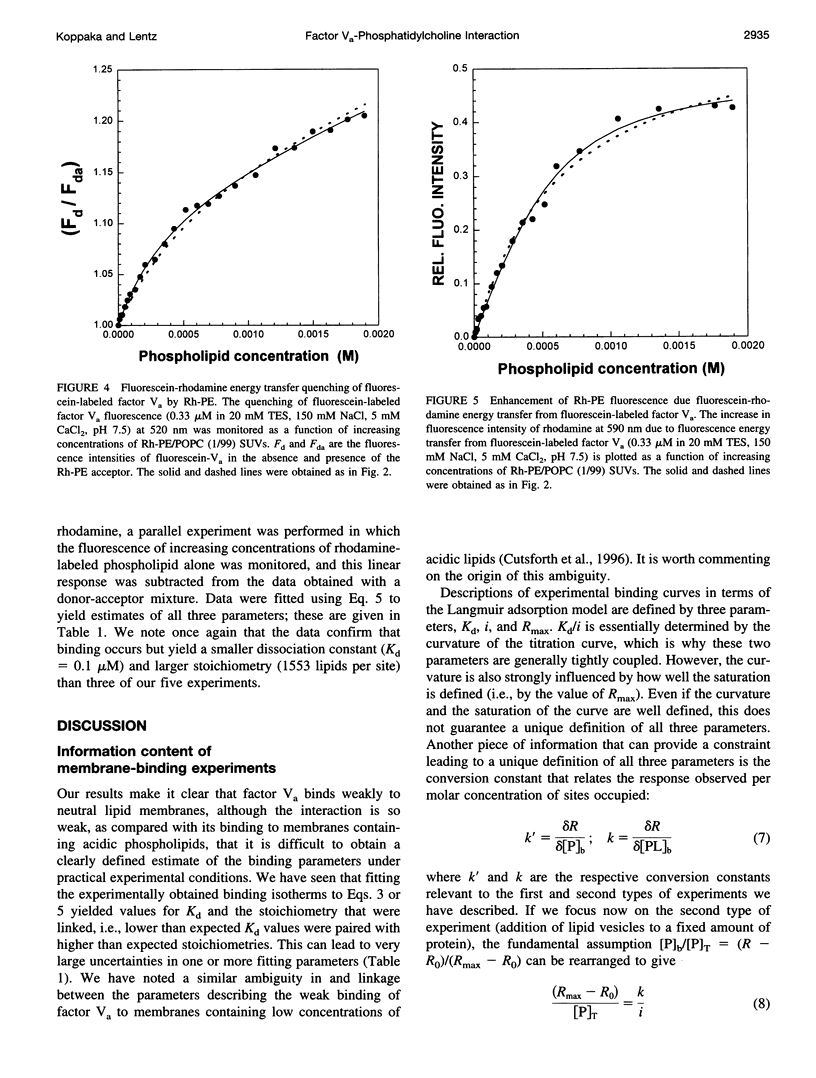
The interaction of bovine factor Va with phosphatidylcholine membranes was examined using four different fluorescence techniques: 1) changes in the fluorescence anisotropy of the fluorescent membrane probe 1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene (DPH) to monitor the interaction of factor Va with 1,2-dimyristoyl-3-sn-phosphatidylcholine (DMPC) small unilamellar vesicles (SUVs), 2) changes in the fluorescence anisotropy of N-(lissamine rhodamine B sulfonyl) diacyl phosphati-dylethanolamine (Rh-PE) incorporated into SUVs prepared from 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-3-sn-phosphatidylcholine (POPC), 3) changes in the fluorescence anisotropy of fluorescein-labeled factor Va (labeled in the heavy chain) upon interaction with POPC SUVs, 4) fluorescence energy transfer from fluorescein-labeled factor Va to rhodamine-labeled POPC SUVs. In the first two sets of experiments, labeled lipid vesicles were titrated with unlabeled protein, whereas, in the latter two types of experiments, labeled factor Va was titrated with vesicles. For the weak binding observed here, it was impossible from any one binding experiment to obtain precise estimates of the three parameters involved in modeling the lipid-protein interaction, namely, the dissociation constant Kd, the stoichiometry of binding i, and the saturation value of the observable Rmax from any one experiment. However, a global analysis of the four data sets involving POPC SUVs yielded a stable estimate of the binding parameters (Kd of approximately 3.0 microM and a stoichiometry of approximately 200 lipids per bound factor Va). Binding to DMPC SUVs may be of slightly higher affinity. These observations support the contention that association of factor Va with a membrane involves a significant acidic-lipid-independent interaction along with the more commonly accepted acidic-lipid-dependent component of the total binding free energy.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Esmon C. T. The subunit structure of thrombin-activated factor V. Isolation of activated factor V, separation of subunits, and reconstitution of biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):964–973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerads I., Govers-Riemslag J. W., Tans G., Zwaal R. F., Rosing J. Prothrombin activation on membranes with anionic lipids containing phosphate, sulfate, and/or carboxyl groups. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 28;29(34):7967–7974. doi: 10.1021/bi00486a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govers-Riemslag J. W., Janssen M. P., Zwaal R. F., Rosing J. Prothrombin activation on dioleoylphosphatidylcholine membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Feb 15;220(1):131–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUZMANN W. Some factors in the interpretation of protein denaturation. Adv Protein Chem. 1959;14:1–63. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60608-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalafatis M., Jenny R. J., Mann K. G. Identification and characterization of a phospholipid-binding site of bovine factor Va. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21580–21589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalafatis M., Rand M. D., Mann K. G. Factor Va-membrane interaction is mediated by two regions located on the light chain of the cofactor. Biochemistry. 1994 Jan 18;33(2):486–493. doi: 10.1021/bi00168a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane W. H., Majerus P. W. Purification and characterization of human coagulation factor V. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1002–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaswamy S., Mann K. G. The binding of factor Va to phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5714–5723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaswamy S., Russell G. D., Mann K. G. The reassociation of factor Va from its isolated subunits. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3160–3168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaswamy S., Williams E. B., Mann K. G. The binding of activated protein C to factors V and Va. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9684–9693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecompte M. F., Bouix G., Mann K. G. Electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions are involved in factor Va binding to membranes containing acidic phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1905–1910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecompte M. F., Krishnaswamy S., Mann K. G., Nesheim M. E., Gitler C. Membrane penetration of bovine factor V and Va detected by labeling with 5-iodonaphthalene-1-azide. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):1935–1937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz B. R., Alford D. R., Hoechli M., Dombrose F. A. Phase behavior of mixed phosphatidylglycerol/phosphatidylcholine multilamellar and unilamellar vesicles. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 31;21(18):4212–4219. doi: 10.1021/bi00261a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz B. R., Barenholz Y., Thompson T. E. Fluorescence depolarization studies of phase transitions and fluidity in phospholipid bilayers. 1. Single component phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4521–4528. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Foster W. B., Hewick R., Mann K. G. Characterization of Factor V activation intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3187–3196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Katzmann J. A., Tracy P. B., Mann K. G. Factor V. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):249–274. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. Thrombin-catalyzed activation of single chain bovine factor V. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1326–1334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odegaard B., Mann K. Proteolysis of factor Va by factor Xa and activated protein C. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11233–11238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortel T. L., Devore-Carter D., Quinn-Allen M., Kane W. H. Deletion analysis of recombinant human factor V. Evidence for a phosphatidylserine binding site in the second C-type domain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):4189–4198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Dahlbäck B., Stenflo J. Thrombin-catalyzed activation of human coagulation factor V. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6556–6564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy P. B., Mann K. G. Prothrombinase complex assembly on the platelet surface is mediated through the 74,000-dalton component of factor Va. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2380–2384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff M., Rodbard D., Chrambach A. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate-containing buffers using multiphasic buffer systems: properties of the stack, valid Rf- measurement, and optimized procedure. Anal Biochem. 1977 Apr;78(2):459–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


