Abstract
The mechanism of binding of blood coagulation cofactor factor Va to acidic-lipid-containing membranes has been addressed. Binding isotherms were generated at room temperature using the change in fluorescence anisotropy of pyrene-labeled bovine factor Va to detect binding to sonicated membrane vesicles containing either bovine brain phosphatidylserine (PS) or 1,2-dioleoyl-3-sn-phosphatidylglycerol (DOPG) in combination with 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-3-sn-phosphatidylcholine (POPC). The composition of the membranes was varied from 0 to 40 mol% for PS/POPC and from 0 to 65 mol % for DOPG/POPC membranes. Fitting the data to a classical Langmuir adsorption model yielded estimates of the dissociation constant (Kd) and the stoichiometry of binding. The values of Kd defined in this way displayed a maximum at low acidic lipid content but were nearly constant at intermediate to high fractions of acidic lipid. Fitting the binding isotherms to a two-process binding model (nonspecific adsorption in addition to binding of acidic lipids to sites on the protein) suggested a significant acidic-lipid-independent binding affinity in addition to occupancy of three protein sites that bind PS in preference to DOPG. Both analyses indicated that interaction of factor Va with an acidic-lipid-containing membrane is much more complex than those of factor Xa or prothrombin. Furthermore, a change in the conformation of bound pyrene-labeled factor Va with surface concentration of acidic lipid was implied by variation of both the saturating fluorescence anisotropy and the binding parameters with the acidic lipid content of the membrane. Finally, the results cannot support the contention that binding occurs through nonspecific adsorption to a patch or domain of acidic lipids in the membrane. Factor Va is suggested to associate with membranes by a complex process that includes both acidic-lipid-specific and acidic-lipid-independent sites and a protein structure change induced by occupancy of acidic-lipid-specific sites on the factor Va molecule.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barenholz Y., Gibbes D., Litman B. J., Goll J., Thompson T. E., Carlson R. D. A simple method for the preparation of homogeneous phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 14;16(12):2806–2810. doi: 10.1021/bi00631a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazzi M. D., Nelsestuen G. L. Extensive segregation of acidic phospholipids in membranes induced by protein kinase C and related proteins. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 13;30(32):7961–7969. doi: 10.1021/bi00246a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birrell G. B., Griffith O. H. Cytochrome c induced lateral phase separation in a diphosphatidylglycerol-steroid spin-label model membrane. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2925–2929. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom J. W., Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. Phospholipid-binding properties of bovine factor V and factor Va. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 2;18(20):4419–4425. doi: 10.1021/bi00587a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boskovic D. S., Giles A. R., Nesheim M. E. Studies of the role of factor Va in the factor Xa-catalyzed activation of prothrombin, fragment 1.2-prethrombin-2, and dansyl-L-glutamyl-glycyl-L-arginine-meizothrombin in the absence of phospholipid. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10497–10505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comfurius P., Smeets E. F., Willems G. M., Bevers E. M., Zwaal R. F. Assembly of the prothrombinase complex on lipid vesicles depends on the stereochemical configuration of the polar headgroup of phosphatidylserine. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 30;33(34):10319–10324. doi: 10.1021/bi00200a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutsforth G. A., Whitaker R. N., Hermans J., Lentz B. R. A new model to describe extrinsic protein binding to phospholipid membranes of varying composition: application to human coagulation proteins. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7453–7461. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutsforth G. A., Whitaker R. N., Hermans J., Lentz B. R. A new model to describe extrinsic protein binding to phospholipid membranes of varying composition: application to human coagulation proteins. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7453–7461. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Owen W. G., Duiguid D. L., Jackson C. M. The action of thrombin on blood clotting factor V: conversion of factor V to a prothrombin-binding protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 17;310(1):289–294. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The subunit structure of thrombin-activated factor V. Isolation of activated factor V, separation of subunits, and reconstitution of biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):964–973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinto E. R., Esmon C. T. Loss of prothrombin and of factor Xa-factor Va interactions upon inactivation of factor Va by activated protein C. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13986–13992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. L., Mann K. G. The interaction of bovine factor V and factor V-derived peptides with phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6503–6508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J., Swanson J. E., Dibble A. R., Hinderliter A. K., Feigenson G. W. Nonideal mixing of phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylcholine in the fluid lamellar phase. Biophys J. 1993 Feb;64(2):413–425. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81382-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husten E. J., Esmon C. T., Johnson A. E. The active site of blood coagulation factor Xa. Its distance from the phospholipid surface and its conformational sensitivity to components of the prothrombinase complex. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):12953–12961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs B. S., Husten E. J., Esmon C. T., Johnson A. E. A domain of membrane-bound blood coagulation factor Va is located far from the phospholipid surface. A fluorescence energy transfer measurement. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 26;25(17):4958–4969. doi: 10.1021/bi00365a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
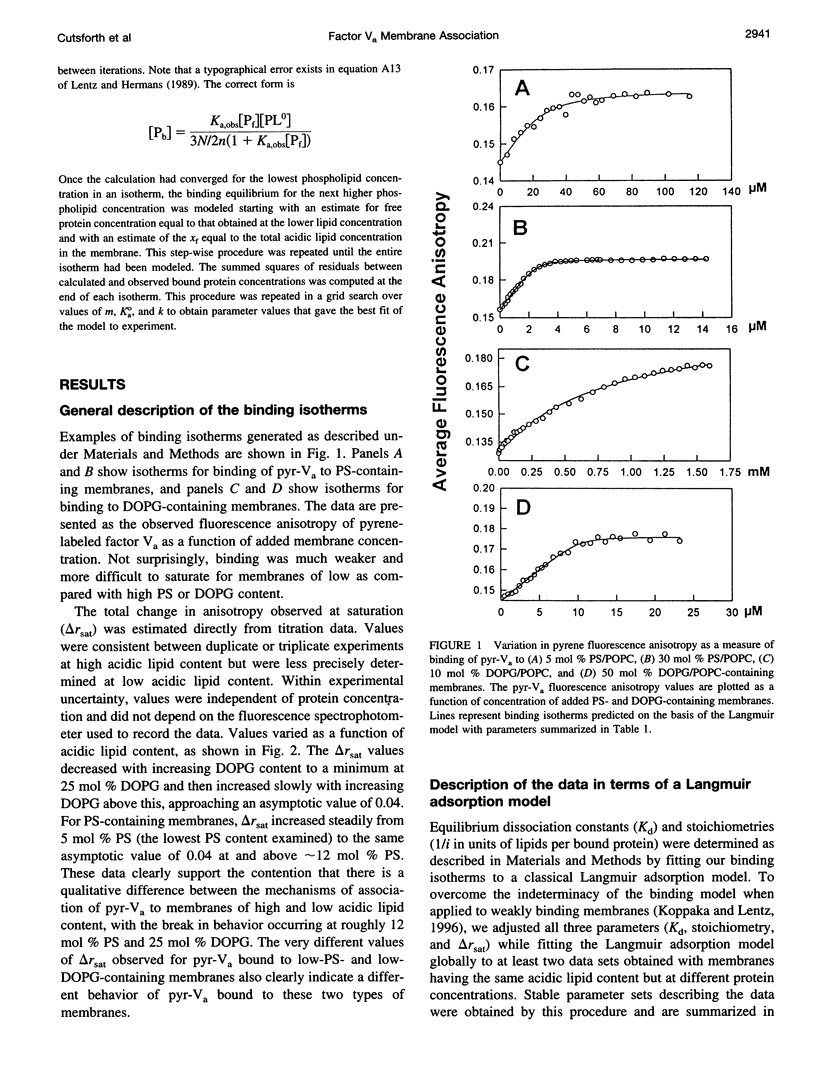
- Jones M. E., Lentz B. R., Dombrose F. A., Sandberg H. Comparison of the abilities of synthetic and platelet-derived membranes to enhance thrombin formation. Thromb Res. 1985 Sep 15;39(6):711–724. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90255-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. E., Lentz B. R. Phospholipid lateral organization in synthetic membranes as monitored by pyrene-labeled phospholipids: effects of temperature and prothrombin fragment 1 binding. Biochemistry. 1986 Feb 11;25(3):567–574. doi: 10.1021/bi00351a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junker M., Creutz C. E. Ca(2+)-dependent binding of endonexin (annexin IV) to membranes: analysis of the effects of membrane lipid composition and development of a predictive model for the binding interaction. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 2;33(30):8930–8940. doi: 10.1021/bi00196a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalafatis M., Jenny R. J., Mann K. G. Identification and characterization of a phospholipid-binding site of bovine factor Va. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21580–21589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalafatis M., Rand M. D., Mann K. G. Factor Va-membrane interaction is mediated by two regions located on the light chain of the cofactor. Biochemistry. 1994 Jan 18;33(2):486–493. doi: 10.1021/bi00168a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Mosior M., Chung L. A., Wu H., McLaughlin S. Binding of peptides with basic residues to membranes containing acidic phospholipids. Biophys J. 1991 Jul;60(1):135–148. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82037-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg U. C., Isaacs B. S., Yemul S. S., Esmon C. T., Bayley H., Johnson A. E. Interaction of blood coagulation factor Va with phospholipid vesicles examined by using lipophilic photoreagents. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 13;26(1):103–109. doi: 10.1021/bi00375a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaswamy S., Jones K. C., Mann K. G. Prothrombinase complex assembly. Kinetic mechanism of enzyme assembly on phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3823–3834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaswamy S., Mann K. G. The binding of factor Va to phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5714–5723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
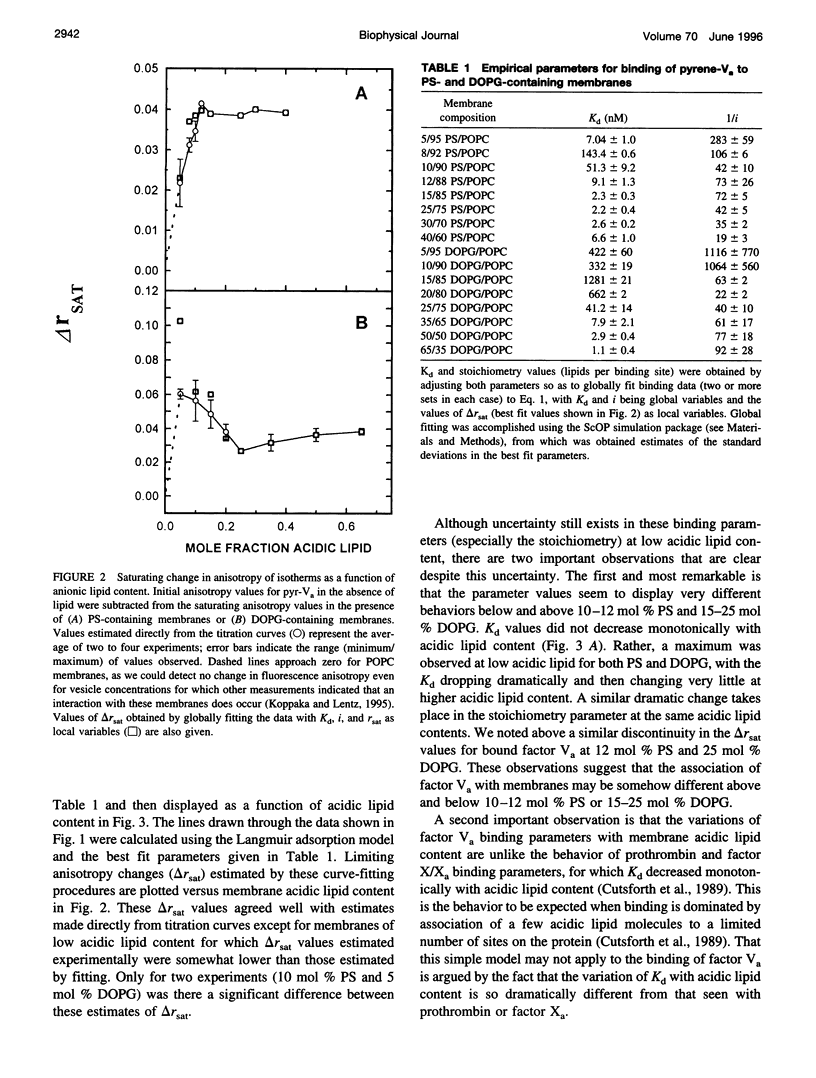
- Krishnaswamy S., Russell G. D., Mann K. G. The reassociation of factor Va from its isolated subunits. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3160–3168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaswamy S., Williams E. B., Mann K. G. The binding of activated protein C to factors V and Va. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9684–9693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampe P. D., Pusey M. L., Wei G. J., Nelsestuen G. L. Electron microscopy and hydrodynamic properties of blood clotting factor V and activation fragments of factor V with phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9959–9964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecompte M. F., Bouix G., Mann K. G. Electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions are involved in factor Va binding to membranes containing acidic phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1905–1910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecompte M. F., Krishnaswamy S., Mann K. G., Nesheim M. E., Gitler C. Membrane penetration of bovine factor V and Va detected by labeling with 5-iodonaphthalene-1-azide. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):1935–1937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz B. R., Alford D. R., Hoechli M., Dombrose F. A. Phase behavior of mixed phosphatidylglycerol/phosphatidylcholine multilamellar and unilamellar vesicles. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 31;21(18):4212–4219. doi: 10.1021/bi00261a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz B. R., Alford D. R., Jones M. E., Dombrose F. A. Calcium-dependent and calcium-independent interactions of prothrombin fragment 1 with phosphatidylglycerol/phosphatidylcholine unilamellar vesicles. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 19;24(24):6997–7005. doi: 10.1021/bi00345a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz B. R., McIntyre G. F., Parks D. J., Yates J. C., Massenburg D. Bilayer curvature and certain amphipaths promote poly(ethylene glycol)-induced fusion of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine unilamellar vesicles. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 17;31(10):2643–2653. doi: 10.1021/bi00125a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz B. R., Wu J. R., Sorrentino A. M., Carleton J. N. Membrane binding induces lipid-specific changes in the denaturation profile of bovine prothrombin. A scanning calorimetry study. Biophys J. 1991 Oct;60(4):942–951. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82128-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim T. K., Bloomfield V. A., Nelsestuen G. L. Structure of the prothrombin- and blood clotting factor X-membrane complexes. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4177–4181. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. D., Nelsestuen G. L. Calcium and prothrombin-induced lateral phase separation in membranes. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2457–2463. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Katzmann J. A., Tracy P. B., Mann K. G. Factor V. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):249–274. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Kettner C., Shaw E., Mann K. G. Cofactor dependence of factor Xa incorporation into the prothrombinase complex. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6537–6540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. Thrombin-catalyzed activation of single chain bovine factor V. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1326–1334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Taswell J. B., Mann K. G. The contribution of bovine Factor V and Factor Va to the activity of prothrombinase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10952–10962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odegaard B., Mann K. Proteolysis of factor Va by factor Xa and activated protein C. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11233–11238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPAHADJOPOULOS D., HANAHAN D. J. OBSERVATIONS ON THE INTERACTION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS AND CERTAIN CLOTTING FACTORS IN PROTHROMBIN ACTIVATOR FORMATION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Aug 19;90:436–439. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
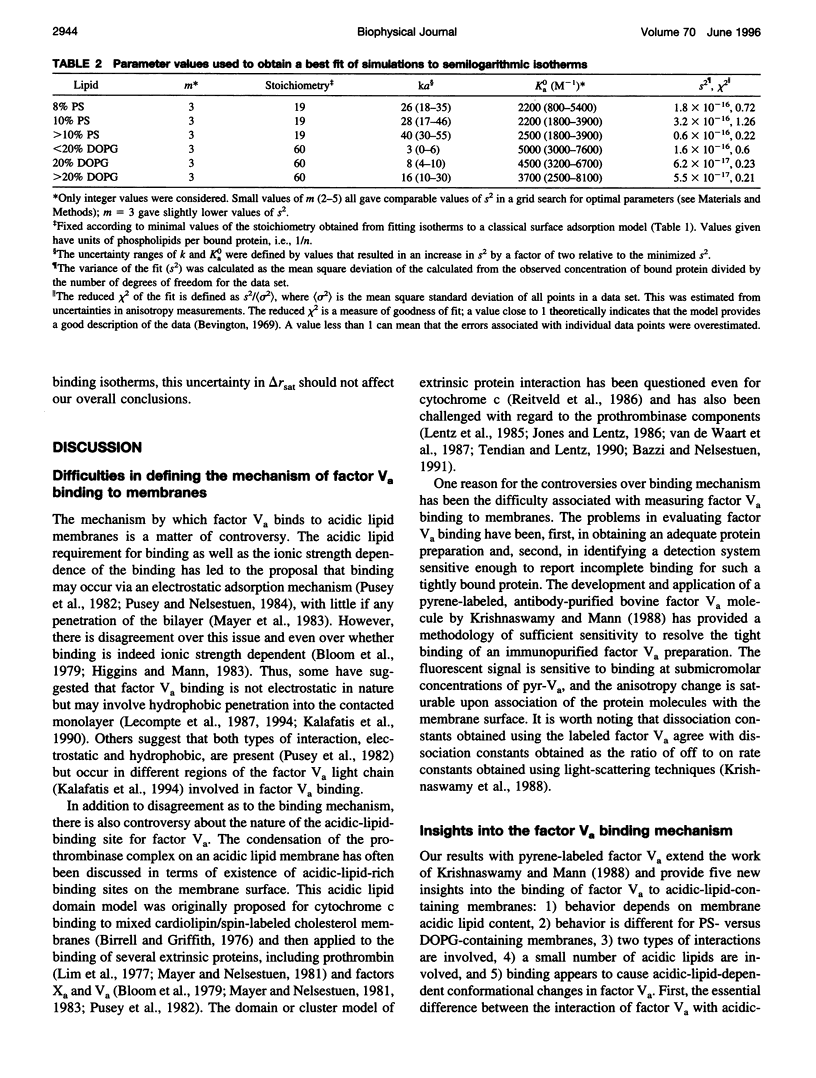
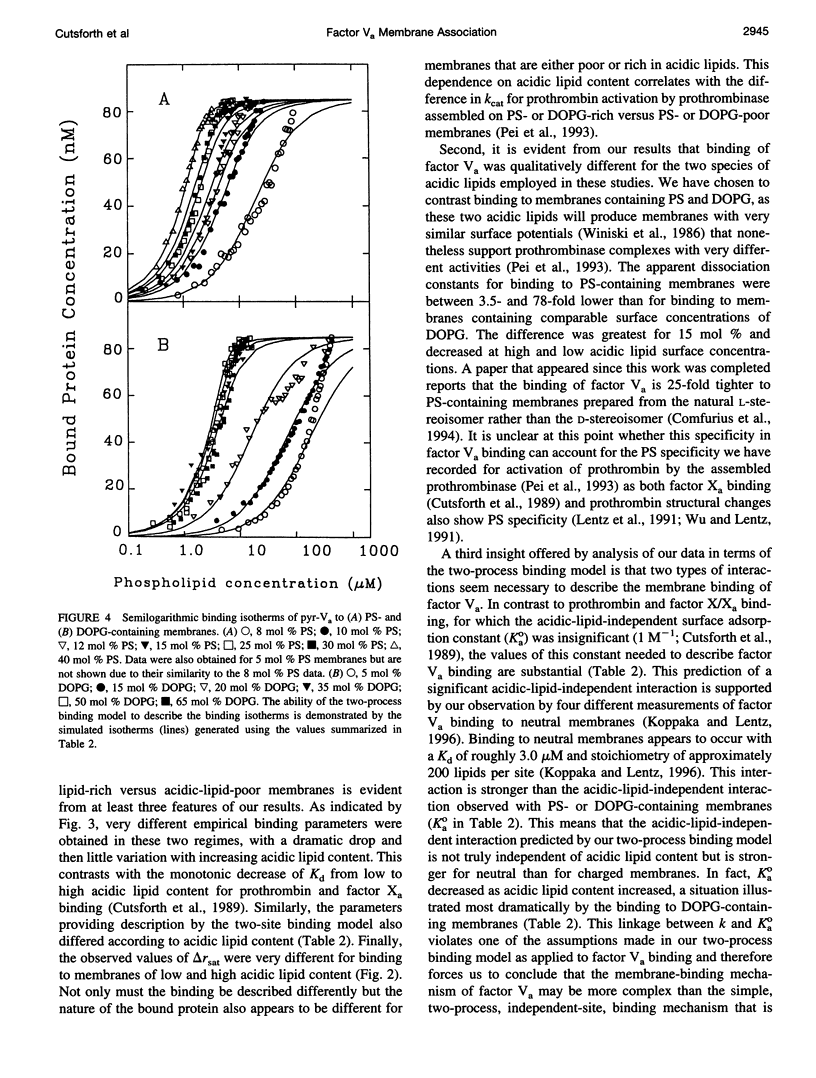
- Pei G., Powers D. D., Lentz B. R. Specific contribution of different phospholipid surfaces to the activation of prothrombin by the fully assembled prothrombinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3226–3233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusey M. L., Mayer L. D., Wei G. J., Bloomfield V. A., Nelsestuen G. L. Kinetic and hydrodynamic analysis of blood clotting factor V-membrane binding. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 12;21(21):5262–5269. doi: 10.1021/bi00264a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusey M. L., Nelsestuen G. L. Membrane binding properties of blood coagulation Factor V and derived peptides. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 4;23(25):6202–6210. doi: 10.1021/bi00320a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietveld A., Berkhout T. A., Roenhorst A., Marsh D., de Kruijff B. Preferential association of apocytochrome c with negatively charged phospholipids in mixed model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 13;858(1):38–46. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90289-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosing J., Bakker H. M., Thomassen M. C., Hemker H. C., Tans G. Characterization of two forms of human factor Va with different cofactor activities. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21130–21136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosing J., Tans G., Govers-Riemslag J. W., Zwaal R. F., Hemker H. C. The role of phospholipids and factor Va in the prothrombinase complex. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):274–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosing J., Tans G., Speijer H., Zwaal R. F. Calcium-independent activation of prothrombin on membranes with positively charged lipids. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 13;27(25):9048–9055. doi: 10.1021/bi00425a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoylova S., Mann K. G., Brisson A. Structure of membrane-bound human factor Va. FEBS Lett. 1994 Sep 12;351(3):330–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00881-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tendian S. W., Lentz B. R. Evaluation of membrane phase behavior as a tool to detect extrinsic protein-induced domain formation: binding of prothrombin to phosphatidylserine/phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 17;29(28):6720–6729. doi: 10.1021/bi00480a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. K., Krishnaswamy S. The activation of prothrombin by the prothrombinase complex. The contribution of the substrate-membrane interaction to catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 4;269(44):27441–27450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winiski A. P., McLaughlin A. C., McDaniel R. V., Eisenberg M., McLaughlin S. An experimental test of the discreteness-of-charge effect in positive and negative lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8206–8214. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. R., Lentz B. R. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic study of Ca2+ and membrane-induced secondary structural changes in bovine prothrombin and prothrombin fragment 1. Biophys J. 1991 Jul;60(1):70–80. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82031-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff M., Rodbard D., Chrambach A. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate-containing buffers using multiphasic buffer systems: properties of the stack, valid Rf- measurement, and optimized procedure. Anal Biochem. 1977 Apr;78(2):459–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Waart P., Bruls H., Hemker H. C., Lindhout T. Interaction of bovine blood clotting factor Va and its subunits with phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2427–2432. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Waart P., Visser A. J., Hemker H. C., Lindhout T. The effect of factor Va on lipid dynamics in mixed phospholipid vesicles as detected by steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence depolarization of diphenylhexatriene. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Apr 15;164(2):337–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11063.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]