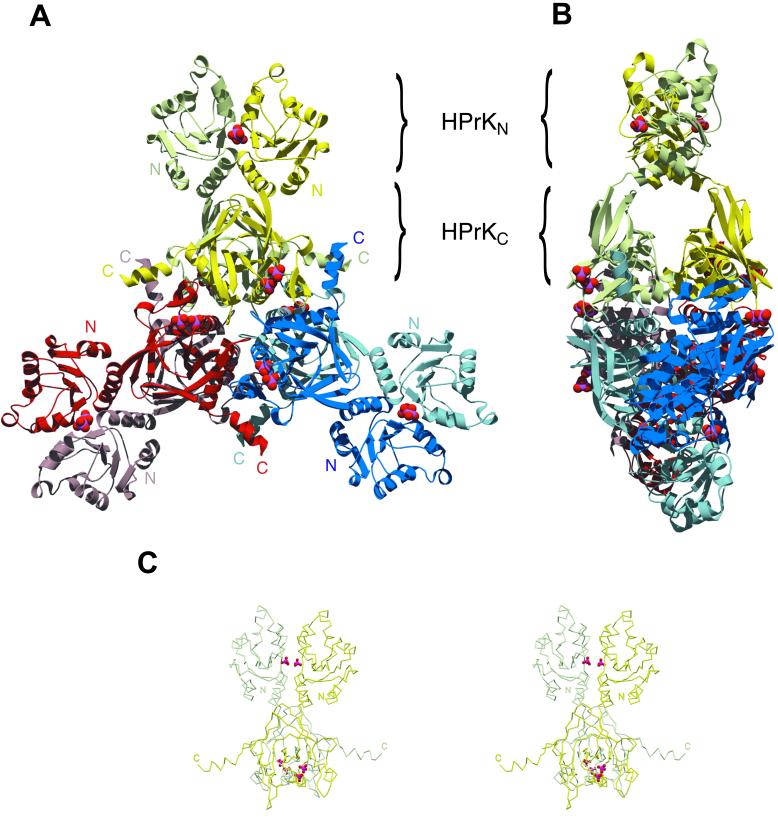
Figure 1.
Structure of the full-length HPr protein kinase from Staphylococcus xylosus. (A) Front view of the HPrK hexamer, composed of three structurally identical dimers deeply intertwined. The kinase domains (HPrKC) occupy the central part of the structure whereas the N-terminal domains (HPrKN) extend outwards as pairwise blades in a propeller. Phosphate ions in the interface between N-terminal domains and P-loop regions are depicted as CPK models. (B) Side view of the hexamer. (C) Stereo view of the HPrK dimer representing the asymmetric unit of the crystal.