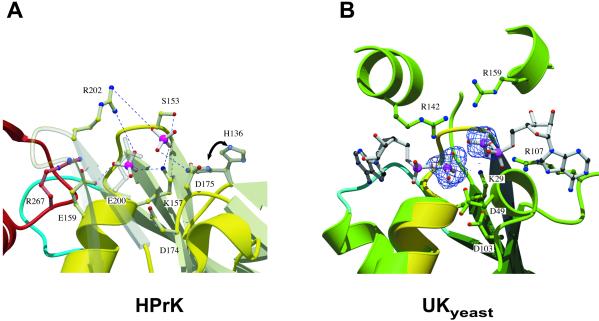
Figure 4.
HPrKC and phosphate binding. (A) Two phosphate ions are bound in the P-loop region, stabilized by invariant residues, most likely involved in catalysis (H136, K157, Ser-153, Glu-159, R202, E200) and/or metal binding (Asp-174/175) (see text). Phosphate 1 occupies the position of the β-phosphate of ATP and is additionally stabilized by water-mediated contacts with R267 from a neighboring subunit. Phosphate 2 (closest to S153) we propose to represent the position of the γ-phosphate of ATP after its transfer to Ser-46 of HPr. Major interactions stabilizing the phosphate ions are shown as blue dashed lines. H136 seems to adopt alternative conformations in the structure, both of which are displayed. (B) P-loop region of HPrKC (yellow) superimposed on the AdK-related UKyeast, bound to two ADP molecules (PDB code 1uky), shown in ball and stick. Electron density corresponding to the two phosphate ions found in HPrKC has been included, matching nearly perfectly the β-phosphate positions of ADP bound to UKyeast. Residues in UKyeast that are structurally equivalent to those in the P-loop of HPrKC are also displayed. K29 and R142 of UKyeast, equivalent to K157 and R202, contact both phosphate ions and are believed to play a role in catalysis through stabilization of transition states. The putative adenine-binding loops are depicted in cyan; the corresponding loop (blue) from neighboring subunit of HPrK is included.