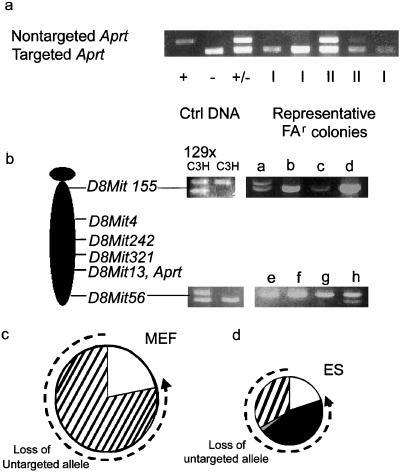
Figure 3.
ES cells and MEFs have distinctly different spectra of mutation. (a) ES cell and MEF variants were designated as class I (loss of the untargeted Aprt allele) or class II (retention of the untargeted Aprt allele) based on allele-specific PCR. PCR of the untargeted Aprt allele yields a 700-bp product; the targeted allele yields a 300-bp product. The +/+, −/−, and +/− controls were derived from wild type, null, and heterozygous (parental) ES cells, respectively. Class I variants and class II variants are designated “I” and “II” below their respective lanes. (b) PCR of informative microsatellite markers was used to define the mechanism of LOH in class I variants. D8Mit155 (1 centimorgan) and D8Mit 56 (73 centimorgan) are markers at the most centromeric and telomeric regions of mouse chromosome 8. 129SvEv × C3H: parental control; C3H: C3H genomic DNA control; a–h: representative FAr class I variants. (c) Distribution of mutation types in MEFs. (d) Distribution of mutation types in ES cells. Dashed line indicates mutagenic mechanisms contributing to loss of the untargeted Aprt allele. □, Point mutation/epigenetic inactivation; ■, chromosome loss and reduplication (nondisjunction); ▨, mitotic recombination; ▩, gene conversion/multilocus deletion/double crossover.