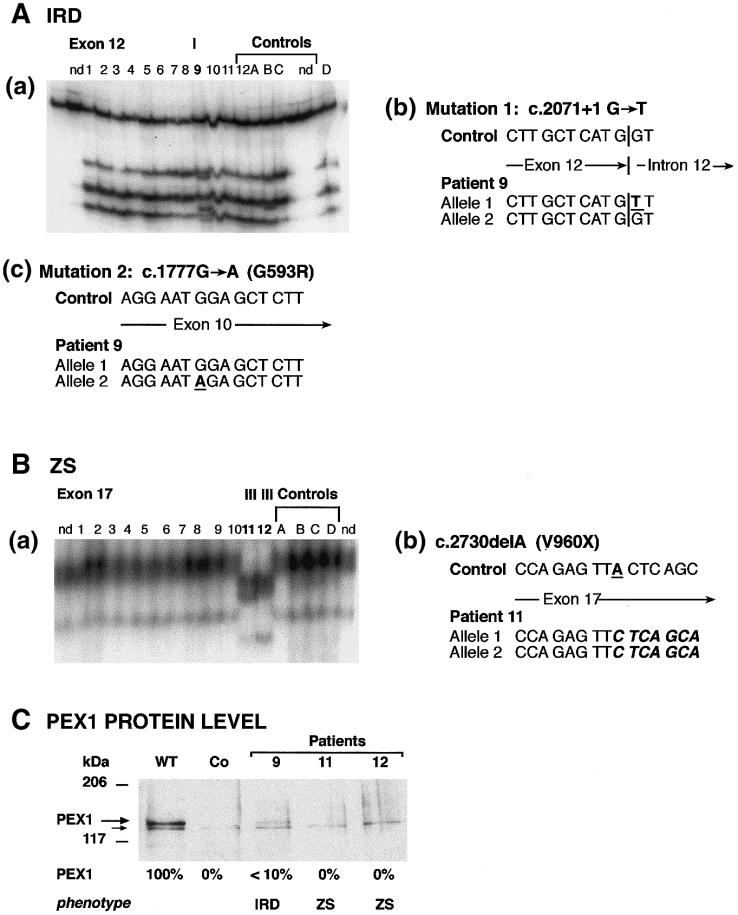
Figure 2.
Genotypes and PEX1 protein levels in patients with IRD and ZS. Abbreviations are as in figure 1. A, Patient 9, affected with IRD: (a) SSCP analysis of exon 12 showed a mobility shift (indicated by “I”); nd = not denatured control, numbers 1–12 indicate CG1 patients 1–12; (b) sequencing of exon 12 led to identification of a G→T transversion at the donor splice site (c.2071+1G→T) in one allele; (c) sequencing of exon 10 revealed one c.1777G→A allele, resulting in G593R. B, Patients 11 and 12, affected with classical ZS: (a) SSCP analysis of exon 17 showed a mobility shift; (b) sequencing revealed a 1-bp deletion of nucleotide 2730 (c.2730delA), resulting in a stop codon at amino acid 960 (V960X). C, The PEX1 protein levels, investigated in cell lysates of patient fibroblasts, given as percentages of the wild-type level. No PEX1 was found in cells of the patients with classical ZS (patients 11 and 12). Approximately 10% of the normal level of PEX1 protein was detected in cells from patient 9, who was affected with the mild clinical phenotype IRD (nonclassical ZS).