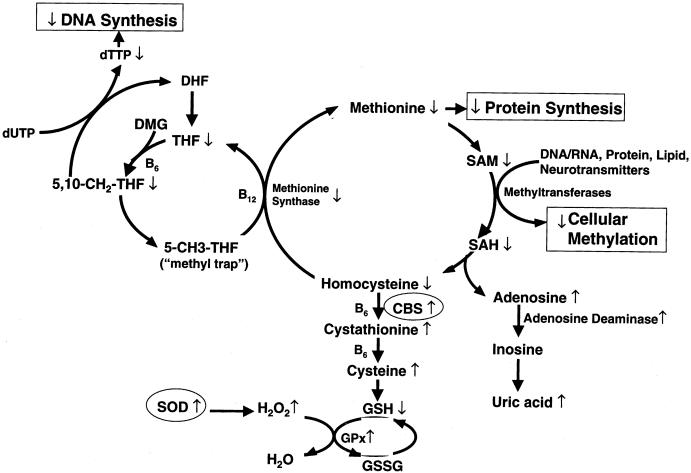
Figure 1.
Overview of interactive and interdependent reactions involved in cellular one-carbon metabolism, with emphasis on the two major metabolic functions of these pathways: normal DNA synthesis/repair and normal cellular methylation reactions. These two major functions intersect at the folate/B12–dependent methionine synthase reaction, which regenerates methionine from homocysteine and, at the same time, generates metabolically active THF for DNA/RNA nucleotide synthesis. Two genes (CBS and SOD) on chromosome 21 that are overexpressed in individuals with DS are shown in circles. Arrows indicate direct and indirect alterations in metabolites, induced by CBS overexpression in individuals with DS.