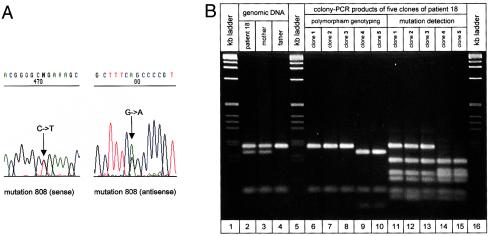
Figure 1.
A, Sequence analysis of patient 18, who is heterozygous for mutation R270X (c.808C→T). The wild-type allele shows the recognition site (GCCG) of the NlaIV restriction enzyme; in the mutant allele, the NlaIV recognition site (GTCG) is abolished. B, Linkage analysis of mutation R270X in patient 18. The status, at the polymorphic region c.377+266C→T of patient 18 and her parents was determined by amplification of the respective region from genomic DNA and subsequent AluI digestion (lanes 2–4). The patient showed a DNA restriction pattern with fragments 195 and 169 bp in length (upper bands), indicating heterozygosity for the c.377+266C→T polymorphism. The patient's father showed a restriction pattern with a 195-bp fragment (missing the 169-bp fragment) indicating that he carries the cytosine variant of the c.377+266C→T polymorphism on his single X chromosome. The patient's mother showed the same restriction pattern as was seen in the patient and is also heterozygous for the c.377+266C→T polymorphism. Conclusively, in patient 18, the allele containing cytosine must be of paternal origin, and the allele containing thymine must be of maternal origin. Lanes 6–15 show polymorphism genotyping and mutation detection in five different clones of patient 18. Clones 1–3 show an AluI restriction pattern indicated by cytosine variant alleles of the c.377+266C→T polymorphism (lanes 6–8), and clones 4 and 5 show a pattern indicated by thymine variant alleles (lanes 9 and 10). Mutation detection in these five clones was done by second-round PCR and subsequent digestion with NlaIV. Mutant alleles miss an NlaIV cleavage site, at position 490 of the generated 590-bp PCR product, resulting in a DNA fragment that is 191 bp in length (upper band), instead of two smaller fragments. Clones 1–3 (lanes 11–13) show this 191-bp fragment, and clones 4 and 5 (lanes 14 and 15) do not. Mutation R270X is linked to the cytosine variant allele of the c.377+266C→T polymorphism and therefore is of paternal origin.