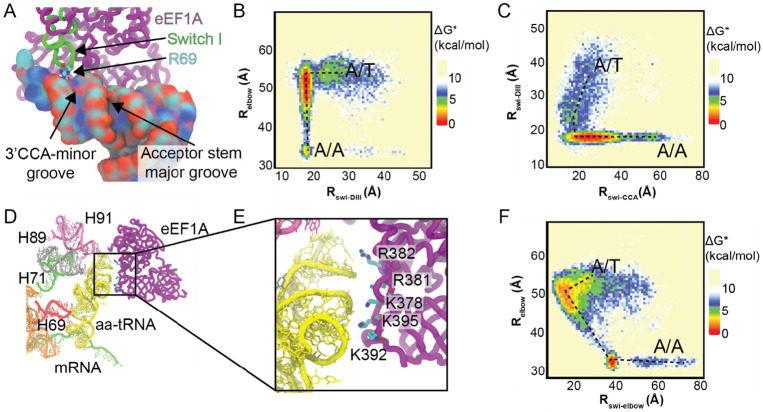
Figure 6. eEF1A interacts with accommodating aa-tRNA through R69 and conserved basic amino acids in Domain III.
(A) R69 of switch I of eEF1A interacts with the minor groove of the aa-tRNA adjacent to the 3’CCA end. R69 is highlighted interacting with the phosphodiester backbone of the tRNA. (B) Approximate free energy landscape of in comparison to the distance between eEF1A R69 and A425 of domain III , generated from potential 2 simulations. This landscape indicates that for aa-tRNA to accommodate, R69 of switch I needs to pass through the 3’CCA-minor groove of the aa-tRNA and dock on domain III. (C) Approximate free energy landscape of with respect to the distance of R69 and A76 of aa-tRNA, generated from potential 2 simulations. This landscape highlights that only the path where R69 passes by the 3’CCA-minor groove is available. (D) Interactions of eEF1A domain III with in proximity to the accommodating aa-tRNA. (E) Zoomed in image of domain III of eEF1A interacting with the accommodating aa-tRNA. Basic amino acids are highlighted that could interact with the aa-tRNA. (F) Approximate free energy landscape of distance with respect to K378 to U55 O3’ distance, generated from potential 2 simulations. This demonstrates that domain III approaches the accommodating aa-tRNA in all simulations at an of ~52 Å.