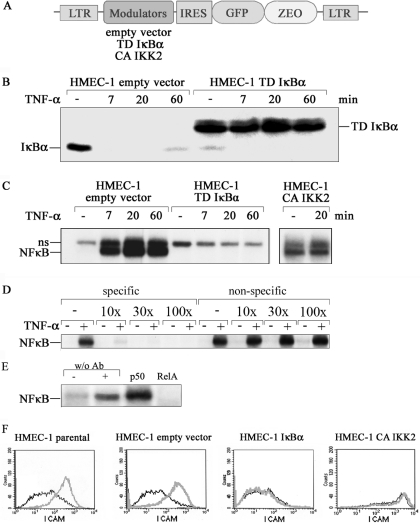
Figure 1.
Genetic manipulation of NF-κB transduced HMEC-1 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the retrovirus used for the expression of the IκBα and IKKβ mutants. IRES, internal ribosome entry site; LTR long terminal repeat: Zeo, zeocin resistance gene; TD, transdominant; CA, constitutively active. (B) Endothelial cells stably expressing parental vector or transdominant IκBα were stimulated with TNF-α for the time intervals indicated. IκBα degradation was visualized by Western blot analysis. (C) TNF-α-induced NF-κB DNA-binding activity was studied by EMSA. NF-κB complexes are indicated; ns, non-specific band. (D) Competition EMSA. Labeled consensus κB probe was incubated with 20 min TNF-α-stimulated or control HMEC-1 whole cell extracts in the presence of increasing amounts of cold probes for consensus kB-probe (specific) or mutated kB-probe (non-specific). (E) Supershift assay. Whole cell extracts of 20 min TNF-α-stimulated or control HMEC-1 were pre-incubated with specific antibodies before NF-κB DNA-binding activity was studied by EMSA. (F) Parental HMEC-1 or cells expressing TD IκBα, CA IKK2 or empty vector, respectively, were stimulated for 16 h with TNF-α. Expression of ICAM was determined by FACS before (black line) or after TNF-α stimulation (grey line).