Figure 3. Physiological expression of Wt. IKKα or IKKα(K44M) in IKKα(−/−) MEFs does not interfere with stimulus dependent NF-κB DNA binding.
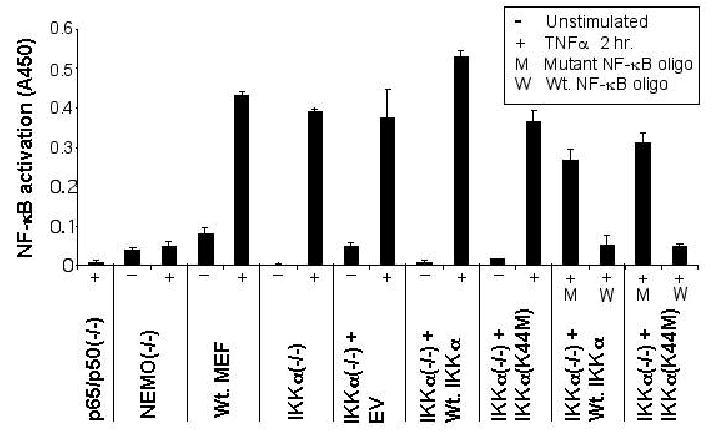
RelA/p65 DNA binding was assayed using the TransAM NF-κB p65 Transcription factor assay kit (Active Motif), following the manufacturer’s instructions for the preparation of nuclear extracts. All samples are presented as (−) unstimulated or (+) stimulated for 2 hours with 20 ng/ml TNFα prior to lysis and nuclear extract preparation. Data shown represent each data point done in quadruplicate, with standard deviations presented as error bars. Nuclear p65 was measured as the absorbance at 450 nm, with a reference wavelength of 650 nm using a fluorescent plate reader. Specificity of p65- DNA binding within the Wt. IKKα and IKKα(K44M) infected populations was determined by competition for binding using an excess of either Wt. (W) or mutant (M) NF-κB synthetic oligonucleotide.
