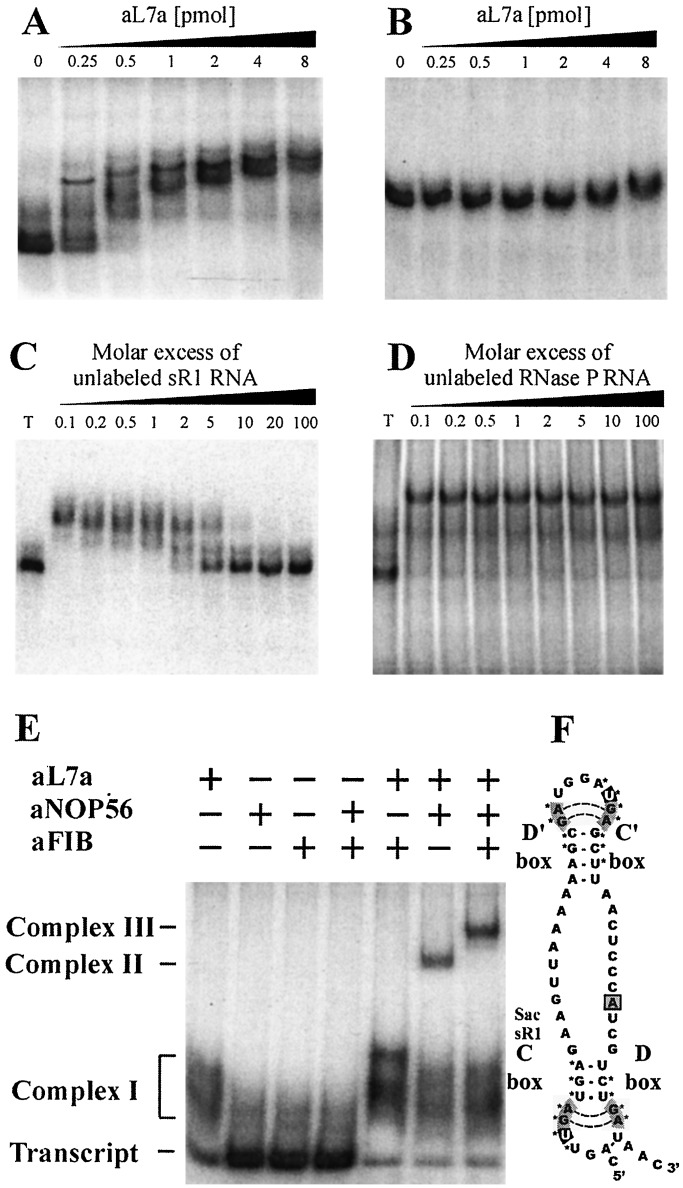
Figure 1.
In vitro assembly of archaeal sR1 sRNA into an RNP complex. In vitro transcribed RNAs were uniformly labeled with [α-32P]ATP and used in gel mobility retardation assays to monitor interaction with recombinant aL7a protein. S. acidocaldarius C/D box sR1 sRNA (0.2 pmol) (A), or RNase P RNA (1 pmol) (B), was mixed with increasing amounts of recombinant aL7a protein (0 to 8 pmol per assay) at 0°C, transferred to 70°C for 10 min, separated on a nondenaturing 10% polyacrylamide gel, and visualized by autoradiography. The competition assays contained radiolabeled sR1 RNA (0.2 pmol), aL7a protein (1 pmol), and nonradiolabeled competitor sR1 (C), or RNase P (D) RNAs (0.02 to 20 pmol). T, transcript. To detect higher-order complexes, uniformly labeled sR1 transcript (0.2 pmol) was mixed with one or more of the proteins (1 pmol of each protein per reaction) at 0°C, transferred to 70°C for 10 min, separated on a nondenaturing 6% polyacrylamide gel, and visualized by autoradiography (E). The positions of free transcript, complex I (sR1 sRNA–aL7a), complex II (sR1 sRNA–aL7a–aNOP56), and complex III (sR1 sRNA–aL7a–aNOP56–aFIB) are indicated. A secondary structural model of sR1s RNA is depicted (F). The aL7a protein is predicted to bind to the loops generated by the C/D or C′/D′ motifs (indicated by *). The base predicted to rotate out of the loop and insert into the pocket of the protein is the first U residue in the C or C′ box sequence and is highlighted in black (20).