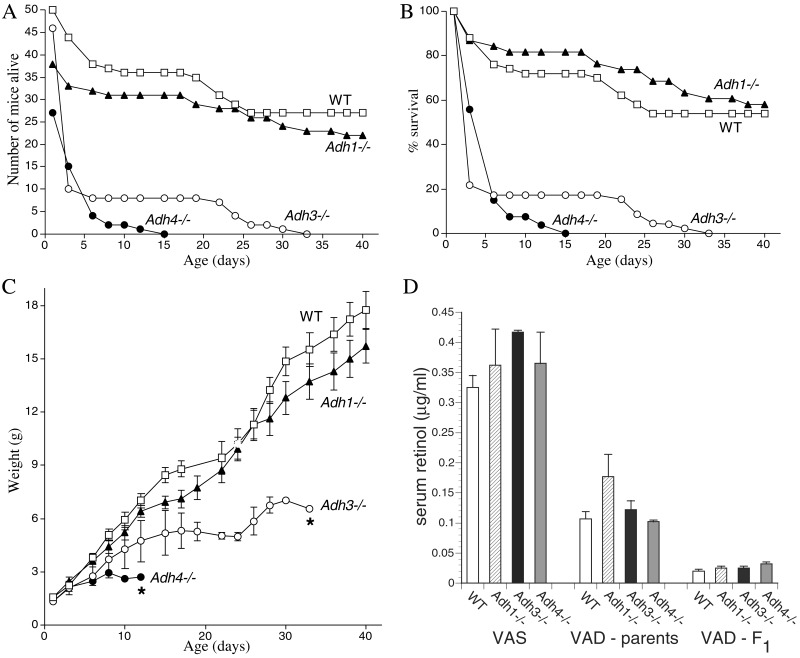
Figure 3.
Adh3−/− mice undergo postnatal lethality during gestational VAD. (A) After exposure to VAD, the number of congenitally VAD F2 generation offspring born for WT mice and each Adh null mutant strain is shown, plus the numbers surviving until postnatal day 40. (B) The previous data are plotted as the percent survival for each mouse strain. Less than 20% survival was observed for Adh3 and Adh4 mutants by postnatal day 6. (C) The weight gain for the WT and null mutant mice above is shown (*, all mice had died by the day indicated). (D) Depletion of serum retinol in WT and Adh null mutant mice during gestational VAD is shown. Serum all-trans-retinol levels were quantitated by HPLC. Control values are shown for 14-week-old vitamin A-sufficient (VAS) female mice (n = 3) maintained on standard mouse chow. Values indicated as VAD-parents refer to the original female parents used to begin the VAD studies (n = 3); these mice were placed on the VAD diet at 6 weeks of age, mated to produce one litter; then at 14weeks of age, serum retinol was measured. Values indicated as VAD-F1 refer to the F1 generation of congenitally VAD female offspring (n = 8) of the original VAD female parents; these females were mated at 6 weeks of age to produce the F2 generation mice described in A–C; then at 14 weeks of age, serum retinol was measured.