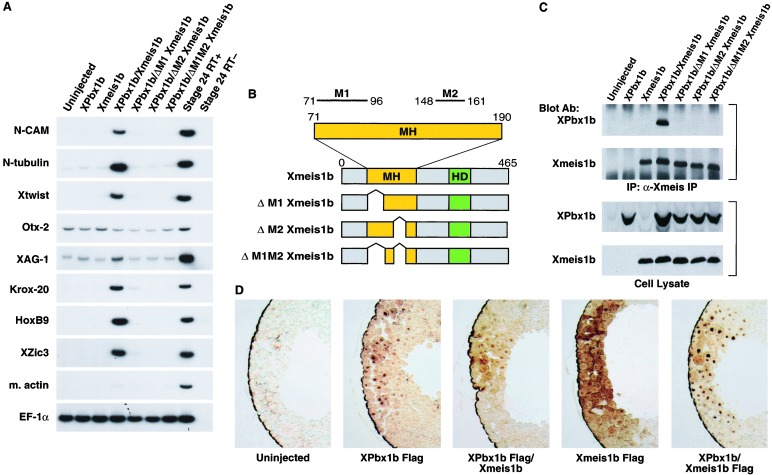
Figure 3.
Interaction of XPbx1b and Xmeis1b induces posterior neural and neural crest markers in animal cap explants in the absence of mesoderm. (A) The animal pole region of two-cell stage embryos were injected with either XPbx1b RNA (1.0 ng per embryo), Xmeis1b RNA (0.5 ng per embryo), or both RNAs. Animal pole explants were excised at stage 9 and cultured until stage 26. RT-PCR gene analysis was performed for N-CAM (pan-neural), N-tubulin (pan-neuronal), Xtwist (neural crest), Otx-2 (forebrain), XAG-1 (cement gland), Krox-20 (hindbrain), HoxB9 (spinal cord), Xzic3 (proneural and early neural crest marker), muscle actin (dorsal mesoderm), and EF-1a (loading control). Stage-24 embryonic RNA with or without reverse transcriptase (RT+ or RT−) also was used as a positive and negative reaction control. Note that coinjection of XPbx1b and Xmeis1b RNA induced the expression of posterior neural and neural crest cell markers. (B) Schematic representation of the Xmeis1b mutants. Wild-type Xmeis1b consists of a Meis-Homothorax domain (MH, yellow box) and homeodomain (HD, green box). MH domain possesses two subdomains: M1 box (amino acids 71–96) and M2 box (amino acids 148–161) that are important for Pbx binding. Deletions of one or more subdomains are indicated. (C) XPbx1b and Xmeis1b physically interact. The animal pole region of two-cell stage embryos were injected with either XPbx1b (2.5 ng per embryo) or Xmeis1b (2.5 ng per embryo) RNA alone or were coinjected with XPbx1b and Xmeis1b wild-type and mutant RNAs. Embryos were cultured until stage 9, and embryonic extracts were prepared and either directly immunoblotted (Lower) or immunoprecipitated with an anti-Xmeis1 antibody before immunoblotting (Upper). Anti-Meis1 antibody or anti-Pbx1b antibody was used to detect the indicated protein. Note: the Xpbx1b protein was coimmunoprecipitated with the wild-type Xmeis1b but not with any of the Xmeis1b mutants. (D) Nuclear localization of the Xmeis1b protein depends upon the XPbx1b protein in frog embryonic cells. The animal pole region of two-cell stage embryos was injected with either Flag tagged XPbx1b (2.5 ng per embryo) or Flag-tagged Xmeis1b RNA (2.5 ng per embryo) alone or in combination with Xmeis1b or XPbx1b RNA (2.5 ng per embryo). Injected embryos were fixed at stage 9, embedded, sectioned, and immunostained with anti-Flag antibody. Note that Xmeis1b protein was in the cytoplasm when expressed alone but was localized in the nuclei in the presence of XPbx1b. In contrast, XPbx1b was localized in the nuclei regardless of whether exogenous Xmeis1b was present.