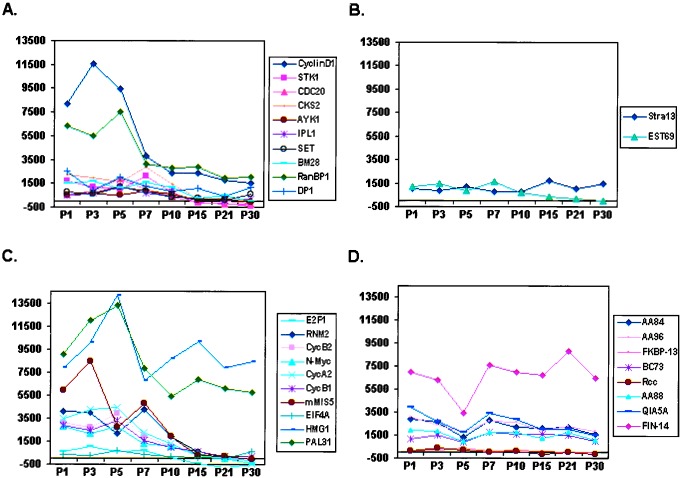
Figure 4.
Temporal analysis of candidate genes/EST expression by whole-organ expression profiling of mouse neonatal cerebellum. (A) Graphical representation of temporal regulation of the 10 of 12 genes from the training set with confirmed expression in the cerebellar EGL (Table 1). Note that they show a similar pattern comprising relatively high levels of expression at PN 3–7 relative to PN 15–30. (B) Temporal analysis of the remaining 2 of 12 genes (Table 1) from the training set. (C and D) Pattern of temporal regulation of 18 additional genes tested (“test set,” Table 1). Note that 8 of 10 genes (C) displayed a similar pattern to genes in A. Conversely, HMG1 exhibited a late peak at PN 15. Seven of nine genes (D) showed a nonspecific temporal pattern of regulation. It should be noted that the failure to identify expression of EST69 and FKBP13 could be because of technical reasons such as faulty probe design or low endogenous levels of expression in vivo. x axis, duplicate samples of mouse cerebella harvested at PNs 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, 15, 21, and 30 were analyzed; y axis, absolute value of Avg Diff as reported by Affymetrix software (scale set at 2,000).