1.
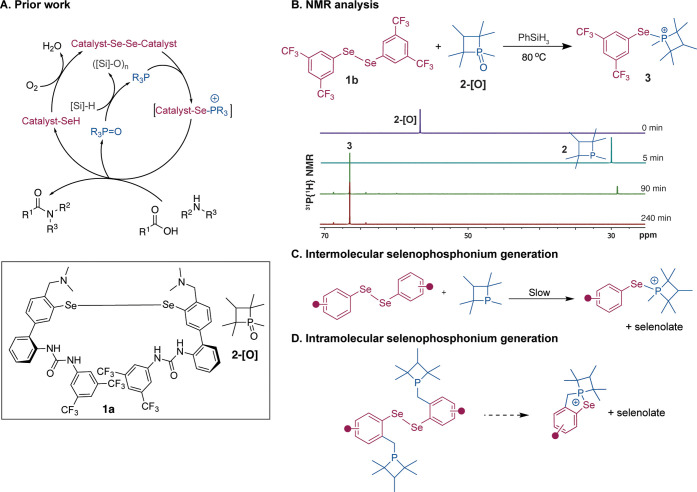
(A) Our previous work on sustainable peptide synthesis showed that a combination of urea diselenide catalyst 1a and phosphetane oxide 2-[O] can lead to catalytic formation of the amide bond. This dual catalytic system utilizes phenylsilane as the terminal reductant and molecular oxygen as the terminal oxidant to drive the catalytic cycle. (B) 31P NMR analysis of key intermediates reveals that the intermolecular reaction between phosphetane 2 and diselenide 1b to generate the key selenophosphonium intermediate 3 is sluggish, requiring approximately 4 h for completion. (C) In the prior work, the selenophosphonium intermediate was generated via an intermolecular reaction between phosphetane 2 and a diaryldiselenide. (D) In the current effort, we developed a small molecule organocatalyst for peptide synthesis wherein the selenophosphonium intermediate is generated through an intramolecular reaction.