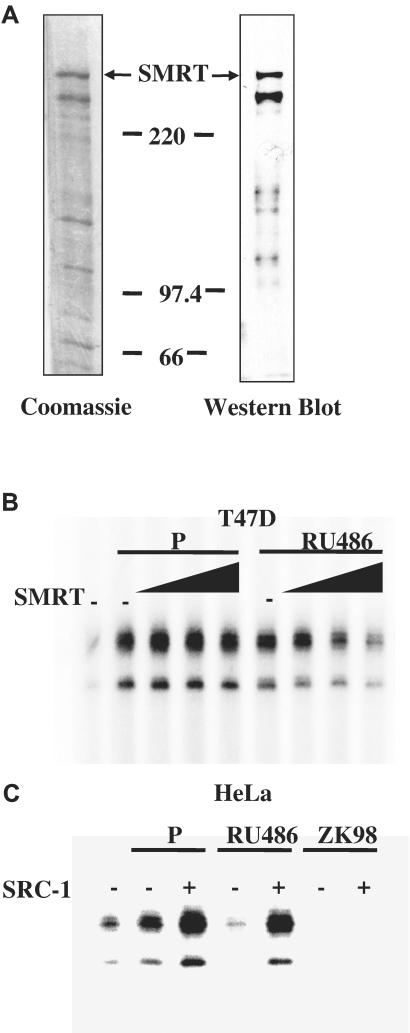
Figure 3.
Coregulators modulated the ability of RU486 to regulate PR transactivation. (A) Purification of human SMRT from baculovirus infected Sf9 cells. The full-length His-6-tagged SMRT was overexpressed in Sf9 cells by using a baculovirus expression system and purified by Ni-NTA affinity chromatography. The recombinant protein was subjected to staining with Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 or Western blot analysis with an antibody specific for SMRT. (B) SMRT preferentially inhibited RU486-stimulated PR transcriptional activity. Chromatin assembly and in vitro transcription reactions were performed with T47D nuclear extracts (NE), P, or RU486 in the presence of increasing concentrations (0, 1, 2.5, or 5 nM) of purified SMRT proteins. (C) SRC-1 enhanced both P- and RU486-dependent PR transcriptional activity. Transcription reactions were carried out by using PR, HeLa NE, P, RU486, or ZK98299 in the presence of purified SRC-1 (1 nM). The final concentration of P, RU486, or ZK98299 was 10−7 M. Results in B and C are representative of three independent experiments. SRC-1 was produced and purified as described.