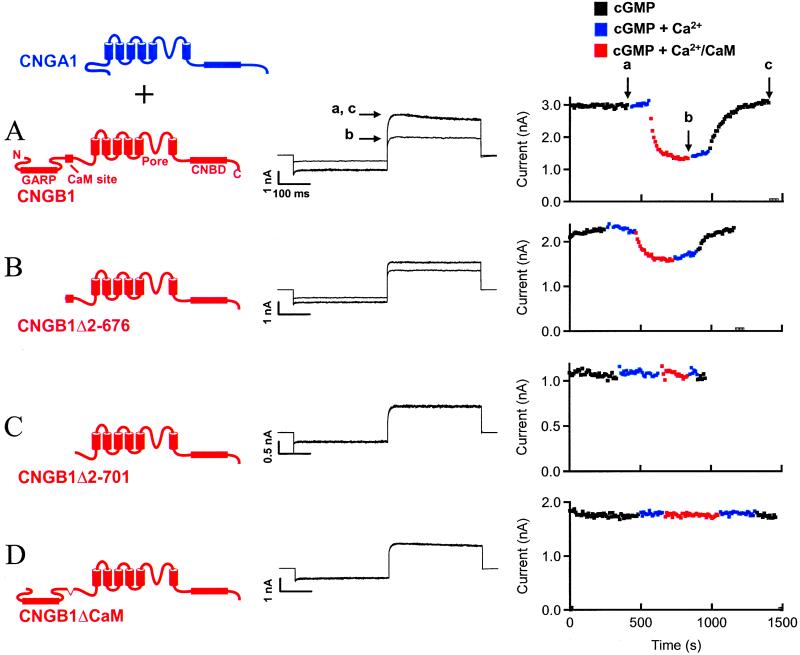
Figure 1.
Localization of a region in rod CNG channels necessary for inhibition by Ca2+/CaM. (A) (Left) Cartoon image depicting coexpression of CNGA1 and CNGB1 subunits. (Center) cGMP-activated currents from wild-type CNGA1/CNGB1 channels in the absence (a and c) and presence (b) of Ca2+/CaM. (Right) Time course of current inhibition by Ca2+/CaM. Arrows labeled a–c indicate points that correspond to the current traces (Center). (B) cGMP-activated currents from CNGA1/CNGB1Δ2–676 channels and time course of inhibition in the presence of Ca2+/CaM. (C) Lack of effect of Ca2+/CaM on CNGA1/CNGB1Δ2–701 channels. (D) Lack of effect of Ca2+/CaM on CNGA1/CNGB1ΔCaM channels. Several CNG channel domains are labeled in A. GARP, glutamic acid-rich protein.