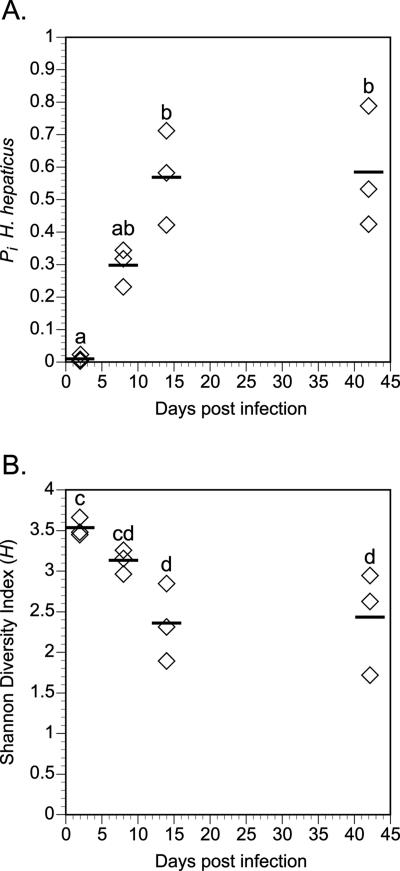
FIG. 6.
Summary of the temporal monitoring of the colonization of the cecae of mice by H. hepaticus. A. The fraction of the total community represented by H. hepaticus (pi, as calculated by T-RFLP analysis) is plotted for the three mice in each experimental group at 2, 8, 14, and 42 days after infection. H. hepaticus is initially a minor component of the mucosa-associated microbiota 2 days after infection but becomes the predominant member of the community by 14 days after infection. B. The Shannon diversity index (H) plotted for the three mice in each experimental group at 2, 8, 14, and 42 days after infection. As the pi of H. hepaticus increases, this is accompanied by a corresponding decrease in the diversity of the mucosa-associated microbiota. Comparisons for all pairs of time points were performed by analysis of variance using Tukey-Kramer HSD. Time points not connected by the same letter are significantly different with an alpha level set to 0.05.