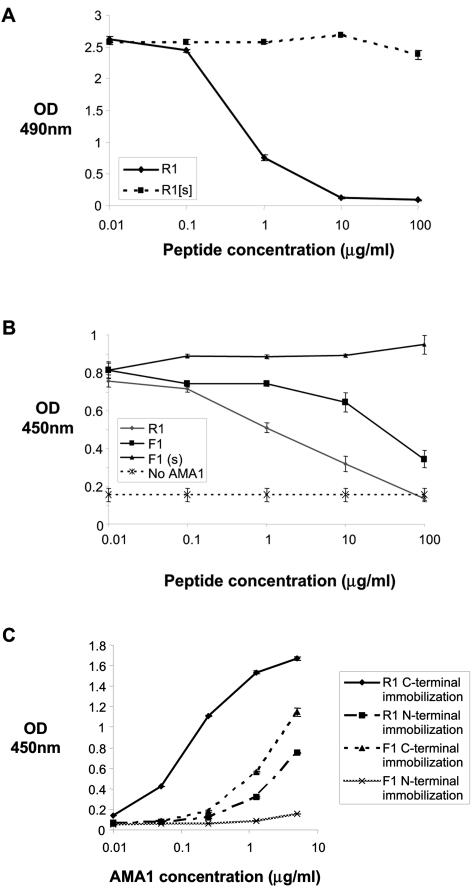
FIG. 3.
Synthetic R1 peptide binds AMA1. (A) Binding of R1 phage to wells coated with AMA1 in the presence of increasing concentrations of synthetic R1 peptide and a synthetic mutated version of the R1 peptide (R1[s]). R1 peptide binds AMA1, but the mutated version does not. (B) The synthetic peptides R1, F1, and F1(s), a scrambled version of the F1 peptide, were tested for their ability to block binding of F1 phage to AMA1. R1 peptide inhibits the interaction between AMA1 and F1 phage more effectively than F1 peptide itself, indicating that R1 and F1 peptides bind similar sites on AMA1. (C) Recombinant AMA1 was incubated with wells coated with R1 and F1 peptides biotinylated at the C or N terminus. AMA1 binds more strongly to C-terminally immobilized R1 peptide.