FIG. 5.
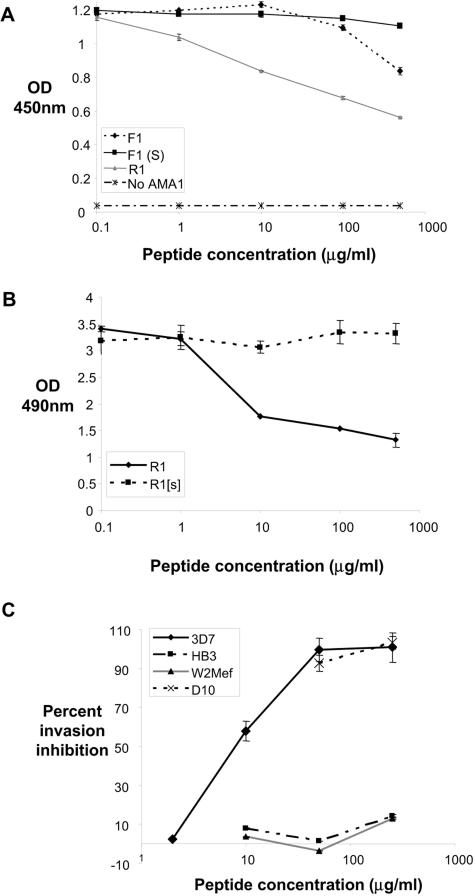
R1 peptide binds a site similar to that bound by inhibitory MAbs 4G2 and 1F9 and blocks parasite invasion of red blood cells. Anti-AMA1 MAbs 4G2 (0.01 μg/ml) (A) and 1F9 (0.05 μg/ml) (B) were allowed to bind immobilized AMA1 in the presence of increasing concentrations of synthetic peptide. The interaction of each of these MAbs with AMA1 is inhibited by the addition of R1 peptide. (C) Percent inhibition of invasion of the 3D7, D10, HB3, and W2mef parasite lines following addition of increasing concentrations of R1 peptide.