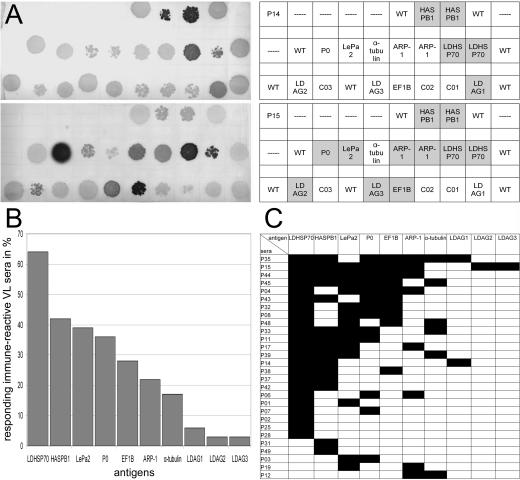
FIG. 1.
Analysis of the frequencies of seropositivity in kala-azar patients from the Kala-Azar Medical Research Center in Muzaffarpur, Bihar, India. The recombinant λ phages for the 10 antigens identified in this study were spotted onto E. coli layers according to the scheme in panel A. After the induction of antigen expression, the antigens were blotted onto nitrocellulose and probed with the sera for antibodies with the corresponding specificities. (A) Examples of the nitrocellulose filters. Replicas of these filters were prepared for and probed with the sera of the patients and healthy controls. The upper filter shown is for patient P14, the lower for patient P15. The charts give the positions of the antigens on the filter. Serodetected antigens are highlighted. For HASPB1, LDHSP70, and ARP-1, two independently identified phage clones were employed. WT, wild-type phages included as negative control; C01 through C03, phages with undefined polyclonal cDNA inserts. (B) Frequencies of seropositivity for the indicated antigens in seroreactive patients. (C) Seroreactivity of the Indian kala-azar patient sera against the identified antigens. Black fields indicate that the patient is seropositive for the corresponding antigen. Only the results for patients who are seropositive for at least 1 of the 10 antigens are shown. Fifteen patients, the 10 healthy relatives of patients, and 11 outgroup individuals (1 from India and 10 from Germany), were seronegative for the antigens.