Figure 1.
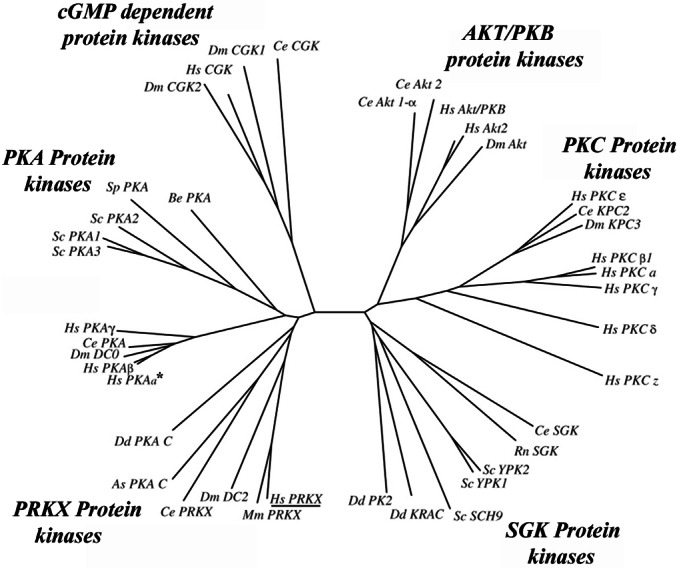
Phylogenetic analysis of the PRKX, PKA, PKC, protein kinase B (PKB), cGMP protein kinases, and serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase (SGK)-related kinase families. The catalytic domains of the most highly PRKX homologous human, nematode, yeast, Dictyostelium, and D. melanogaster protein kinases identified by BLAST search were aligned with CLUSTALW (http://workbench.sdsc.edu/CGI/BW.cgi) to generate an unrooted phylogenetic tree with PHYLIP 3.5C (46). Protein kinase Y (PRKY, GenBank accession no. CAA75792) was excluded, because it lacks 81 C-terminal amino acid residues essential for kinase activity (47). The PKC family was added to the phylogenetic analysis as an outgroup (48). Except for the SGK kinase (from Rattos norvegicus) and mouse PRKX, all mammalian kinases used in this analysis were the human orthologs (see Table 2, which is published as supporting information on the PNAS web site, www.pnas.org). The PKA-α kinase is indicated by an asterisk, and human PRKX is underlined.
