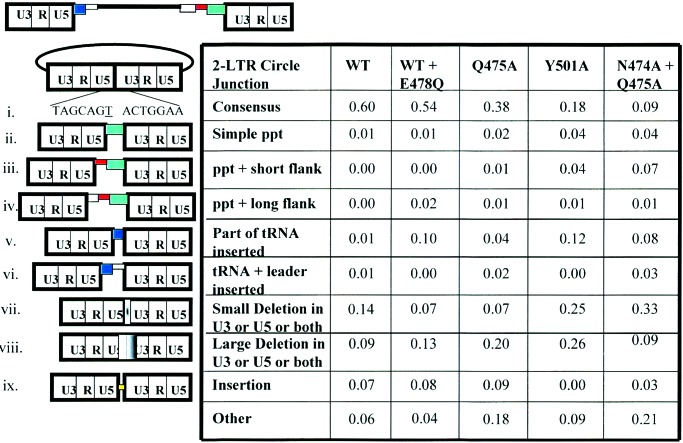
Figure 5.
Frequency of different classes of 2-LTR circle junctions. 2-LTR circle junctions were analyzed from cells infected with the wild-type vector (WT), vector with reduced RNase H activity (WT + E478Q), and vectors containing the RNase H primer grip mutations Q475A, Y501A, and N474A + Q475A. At the top is a schematic diagram of the unintegrated viral DNA. The pbs is shown in navy blue, the viral leader sequence 3′ of the pbs is shown in light blue, the region 5′ of the ppt is shown in gray, the U-tract is red, and the ppt is in green. The drawing is not to scale. (i) The consensus 2-LTR circle junction arising from the ligation of the ends of unintegrated viral DNA. The underlined T is derived from the ribonucleotide A at the 3′ end of the tRNALys-3 primer used for minus-strand DNA synthesis. (ii) “Simple” ppt insertions (green box) that contain part or all of the ppt but no upstream flanking sequences. This class of defective circle junctions may also contain deletions in the U5 region. (iii) Insertion of the ppt (green box) along with short flanking sequences (adjacent red box) immediately upstream of the ppt. These flanking sequences are 1–5 bp in length and are probably caused by improper cleavages by RNase H (see Fig. 6 and Results and Discussion). (iv) Insertion of the ppt with long flanking sequences (gray box) upstream of the ppt. This class of inserts may also include deletions in the U5 region. (v) Insertions of part of the tRNA Lys-3 sequences (blue box) at the 2-LTR circle junction. Only a portion of the tRNA is reverse transcribed and inserted; this portion corresponds to the tRNA sequences that anneal to the pbs. This class of defective circle junctions may also include deletions in the U3 region. (vi) Insertion of tRNA (navy blue box) and viral leader sequence from downstream of the pbs (light blue box). During reverse transcription, plus-strand DNA synthesis is initiated from the ppt primer and copies both the minus-strand DNA and the portion of the tRNA primer that hybridizes to the pbs (Fig. 1). Normally, this plus strand is transferred to the minus strand after the tRNA is removed (see Fig. 1). However, if RNase H fails to remove the tRNA primer before the plus strand is extended a second time to complete the synthesis of viral DNA, the tRNA can be copied a second time. If this happens, the DNA could undergo another strand-transfer reaction, and RT could then copy the adjacent sequences on the leader, which could be captured at the circle junction. This class of defective circle junctions may also include deletions in the U3 region. (vii) Small deletions (1–5 bp) at the circle junction in the U3, U5, or both U3 and U5 (white to black gradation). (viii) Large deletions in the U5, the U3 or both U5 and U3 (white to black box overlapping the circle junction). (ix) Insertions (yellow box) at the 2-LTR circle junction that do not come from either the ppt or the tRNA primer. (x) Deletions with insertions that do not derive from the ppt or the tRNA primer.