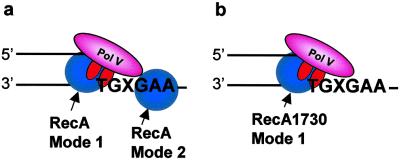
Fig 5.
Model depicting pol V-catalyzed SOS translesion synthesis. (a) Wild-type RecA exhibits two modes of RecA action, mode 1 stimulation of pol V activity when interacting with pol V at the 3′-OH primer end, and mode 2 cocatalysis of translesion synthesis when bound to the DNA template strand at the 5′ side of the lesion, X. (b) Mutant RecA1730 (S117F) exhibits mode 1 stimulation of pol V activity but is essentially unable to cocatalyze translesion synthesis, based on the data in Fig. 2. RecA protein is illustrated as a monomer, but its detailed structure is unknown and could instead be a multimer.