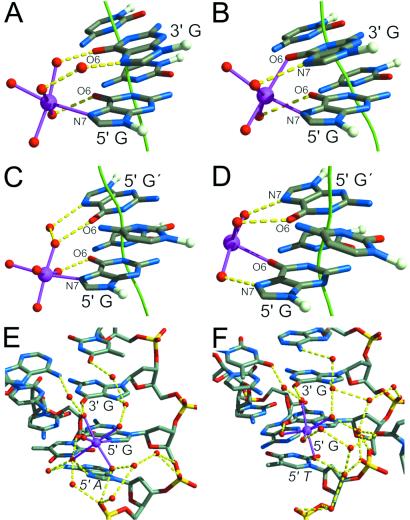
Fig 2.
Three-bond and four-bond modes of Mn2+ binding in the DNA major groove. (A and C) The three-bond mode is shown for sites 1-GG and 5-GC, respectively. (B and D) The four-bond mode is shown for sites 4-GG and 6-GC, respectively. The guanine N7 and O6 atoms defining the metal binding mode and the contributing bases are labeled (G′ indicates the complementary base to C in the GC step). A nonzero shift parameter for a base pair step is visualized as a deviation of the double helix axis (green). Coordination bonds (magenta) between metal ion (magenta) and water molecules (red), and hydrogen bonds (yellow) between bases and first and second shell, coordinated water molecules are shown. (E) The site 1-GG (A) is shown with its full hydrogen bonding network. A hydrogen bond occurs between the N7 atom of the adenine base (5′ A) adjacent to the GG base step and a metal-coordinated water molecule, contributing to the orientation of the metal ion-hydrate. (F) Site 3-GG binds Mn2+ in the same three-bond mode as site 1-GG, but lacks the additional coordination shell bond from the adjacent thymine base (5′ T).