Abstract
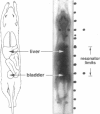
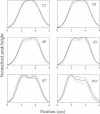
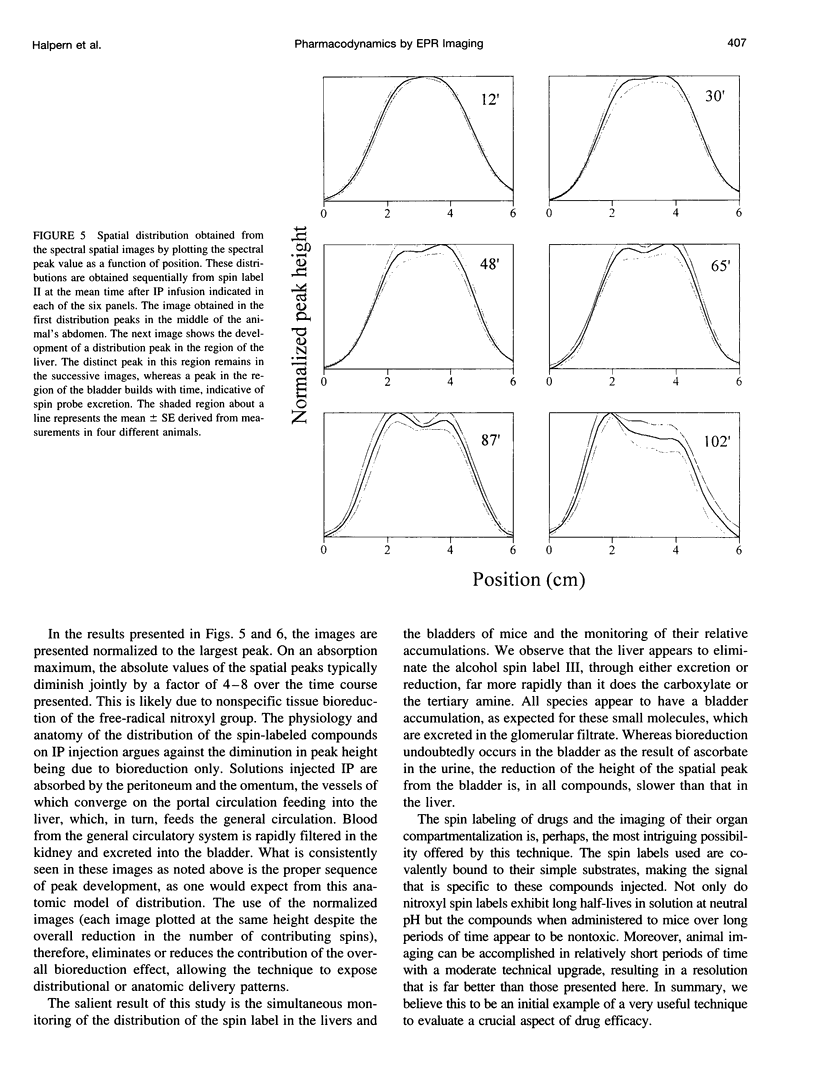
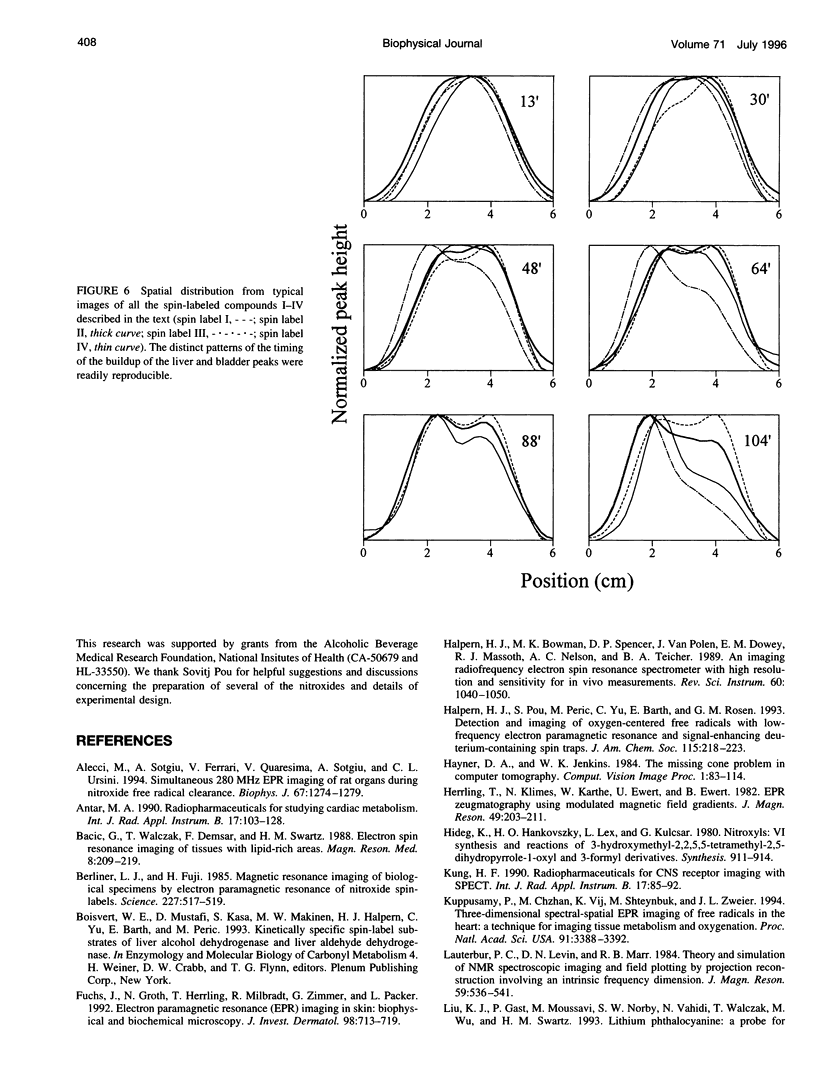
A novel, very-low-frequency electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) technique is used to image the distribution of several nitroxides with distinct pharmacologic compartment affinities in the abdomens of living mice. Image acquisition is sufficiently rapid to allow a time sequence of the distribution for each compound. The spectra and concentrations of these nitroxides are imaged with the use of spectral-spatial imaging to distinguish a single spatial dimension. Liver and bladder of the mouse anatomy are distinguished by this technique. After an intraperitoneal injection of the spin-label probes, a shift in the distribution of the compounds from the upper abdomen (primarily liver) to the lower abdomen (primarily bladder) is observed. The time dependence of the shift in regional distribution depends on the structural properties of the side chain attached to the spin label. These results indicate that this application of in vivo electron paramagnetic resonance imaging will provide a new method of magnetic resonance imaging for determination of pharmacodynamics in the body of an intact animal.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alecci M., Ferrari M., Quaresima V., Sotgiu A., Ursini C. L. Simultaneous 280 MHz EPR imaging of rat organs during nitroxide free radical clearance. Biophys J. 1994 Sep;67(3):1274–1279. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80599-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antar M. A. Radiopharmaceuticals for studying cardiac metabolism. Int J Rad Appl Instrum B. 1990;17(1):103–128. doi: 10.1016/0883-2897(90)90014-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins H. L., Richards P. Assessment of thyroid function and anatomy with technetium-99m as pertechnetate. J Nucl Med. 1968 Jan;9(1):7–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacić G., Walczak T., Demsar F., Swartz H. M. Electron spin resonance imaging of tissues with lipid-rich areas. Magn Reson Med. 1988 Oct;8(2):209–219. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910080211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berliner J. L., Fujii H. Magnetic resonance imaging of biological specimens by electron paramagnetic resonance of nitroxide spin labels. Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):517–519. doi: 10.1126/science.2981437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs J., Groth N., Herrling T., Milbradt R., Zimmer G., Packer L. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) imaging in skin: biophysical and biochemical microscopy. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 May;98(5):713–719. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12499919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung H. F. Radiopharmaceuticals for CNS receptor imaging with SPECT. Int J Rad Appl Instrum B. 1990;17(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0883-2897(90)90012-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppusamy P., Chzhan M., Vij K., Shteynbuk M., Lefer D. J., Giannella E., Zweier J. L. Three-dimensional spectral-spatial EPR imaging of free radicals in the heart: a technique for imaging tissue metabolism and oxygenation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3388–3392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu K. J., Gast P., Moussavi M., Norby S. W., Vahidi N., Walczak T., Wu M., Swartz H. M. Lithium phthalocyanine: a probe for electron paramagnetic resonance oximetry in viable biological systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5438–5442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pou S., Davis P. L., Wolf G. L., Rosen G. M. Use of nitroxides as NMR contrast enhancing agents for joints. Free Radic Res. 1995 Oct;23(4):353–364. doi: 10.3109/10715769509065256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reba R. C. PET and SPECT: opportunities and challenges for psychiatry. J Clin Psychiatry. 1993 Nov;54 (Suppl):26–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röschmann P. Radiofrequency penetration and absorption in the human body: limitations to high-field whole-body nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. Med Phys. 1987 Nov-Dec;14(6):922–931. doi: 10.1118/1.595995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöcklin G. Tracers for metabolic imaging of brain and heart. Radiochemistry and radiopharmacology. Eur J Nucl Med. 1992;19(7):527–551. doi: 10.1007/BF00185860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]