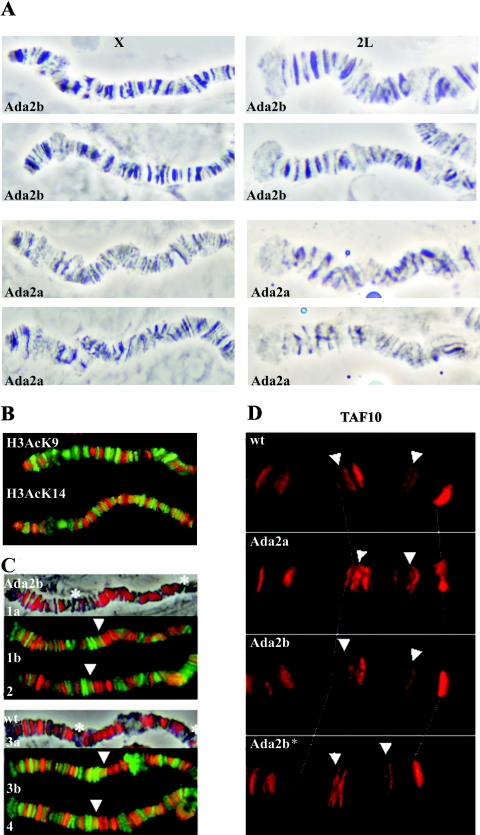
FIG. 3.
(A) Phase-contrast images of X and 2L polytene chromosome regions of Ada2b and Ada2a mutants. Note the distorted banding pattern and less condensed structure of Ada2a chromosomes. (B) Enlarged parts of wild-type X chromosomes coimmunostained for Pol II (green) and acetylated H3 K9 or H3 K14 (red) show identical distributions of H3 K9 and H3 K14 acetylation. (C) Enlarged parts of Ada2b (1a, 1b, and 2) andwild-type (3a, 3b, and 4) 2L chromosomes stained for H3AcK14 (red) and Pol II (1b, 2, 3b, and 4; green). H3AcK14 staining in both wild-type and Ada2b mutants is colocalized mostly, but not exclusively, with bands, while Pol II immunostaining is colocalized with interband regions. The asterisks and arrowheads indicate bands exhibiting weak staining for H3AcK14 and colocalization of H3AcK14 and Pol II, respectively. (In order to allow a comparison of the Ada2b mutant and the wild type, images of H3AcK14-specific antibody-stained chromosomes are color enhanced.) (D) Localization of TAF10 in the 3R region of wild-type and Ada2 polytene chromosomes. Genotypes are indicated in the pictures. Ada2b* is a chromosome from an Ada2b homozygote carrying the Ada2b+ transgene. Arrows point to locations where TAF10 localization in the Ada2b mutant is lost.