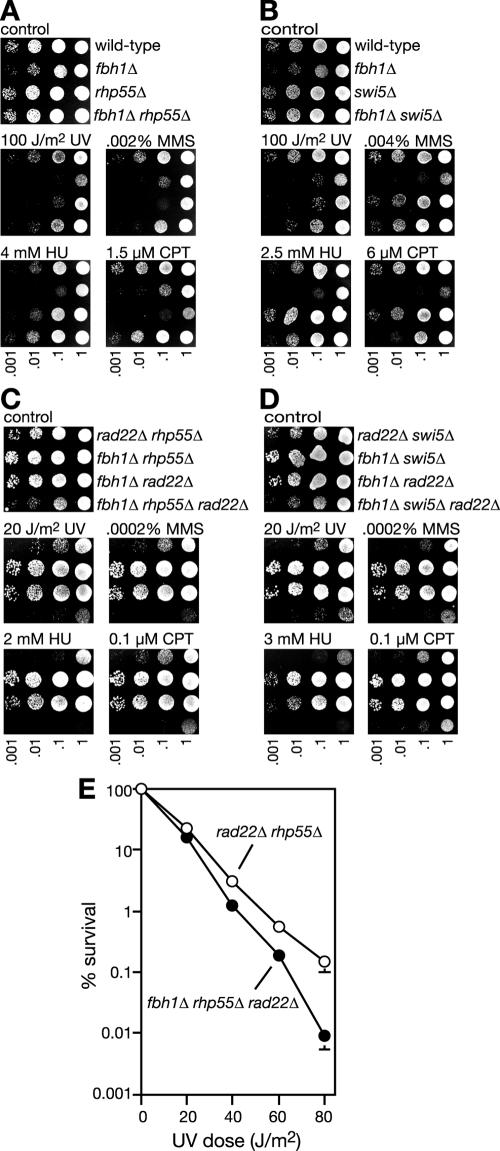
FIG. 6.
Genetic interactions between fbh1 and rhp55 or swi5. (A and B) Spot assays comparing the genotoxin sensitivities of wild-type (MCW1221), fbh1Δ (MCW1490), rhp55Δ (MCW1231), fbh1Δ rhp55Δ (MCW1568), swi5Δ (YA177), and fbh1Δ swi5Δ (MCW1590) strains. The plates were photographed after 3 days of incubation. (C and D) Spot assays assessing the dependence on rhp55 and swi5 for the suppression of rad22Δ genotoxin sensitivity by fbh1Δ. The strains are rad22Δ rhp55Δ (MCW1679), fbh1Δ rhp55Δ (MCW1568), fbh1Δ rad22Δ (MCW1553), fbh1Δ rhp55Δ rad22Δ (MCW1681), rad22Δ swi5Δ (MCW1643), fbh1Δ swi5Δ (MCW1590), and fbh1Δ swi5Δ rad22Δ (MCW1645). The plates were photographed after 5 days of incubation.(E) UV survival curves of rad22Δ rhp55Δ (MCW1679) and fbh1Δ rhp55Δ rad22Δ (MCW1681) strains. The error bars represent the standard deviations about the mean values.