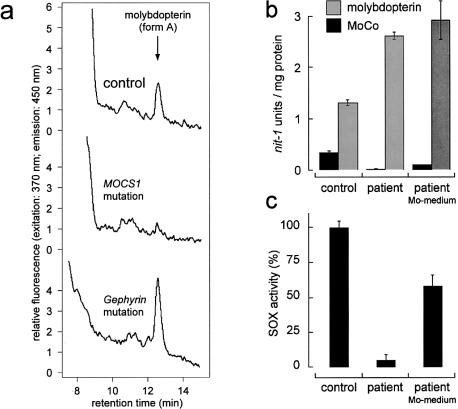
Figure 4.
Biochemical characterization of fibroblasts with the gephyrin gene deletion. a, HPLC detection of the molybdopterin derivative “form A” in crude fibroblast extracts of a healthy control subject (top), a patient with a MOCS1 mutation as negative control (middle), and the patient with the gephyrin gene deletion (bottom). Molybdopterin was detected by conversion to its stable oxidation product form A-dephospho. Oxidation (1 mg protein per sample) with I2/KI, QAE-sephadex chromatography and HPLC analysis on a C18 reversed-phase column were performed as described elsewhere (Schwarz et al. 1997). b, nit-1 reconstitution assay for the detection of active MoCo (−Mo) and total molybdopterin, including both the metal-free and metal-loaded pterin (+Mo) of a control (left) and of the patient without (middle) and with (right) molybdate supplementation of the medium. c, Sulfite oxidase activity of control fibroblasts (left), the patient's fibroblasts grown on normal medium (middle) and the patient's fibroblasts grown on medium supplemented with molybdate (10 mM) (right). Neurospora crassa nit-1 extract was prepared as described elsewhere (Nason et al. 1971). The assay was performed in a 90-μl (+Mo) or a 180-μl (−Mo) volume containing 30 μl or 60 μl, respectively, of nit-1 extract freshly filtered on gel (Nick columns; Amersham/Pharmacia) in the presence of 2 mM reduced glutathione. Protein extracts from fibroblasts were prepared in 50 mM sodium phosphate, 200 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA (pH 7.2) and were added in various amounts (20–120 μl) to the nit-1 extract, according to the linear range of the assay. Total molybdopterin content was determined by performing the reconstitution in the presence of 10 mM sodium molybdate. MoCo was detected in the absence of external molybdate. Complementation was carried out anaerobically overnight at 4°C. After addition of 20 mM NADPH for 10 min, reconstituted NADPH-nitrate reductase activity was determined. One nit-1 unit is defined as the A540 of 1.0/30 min nitrate reductase reaction time. Sulfite oxidase activity was determined as described elsewhere (Johnson et al. 1991).