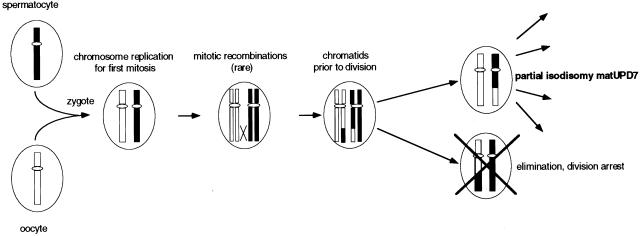
Figure 4.
Mitotic recombinations leading to the partial isodisomic matUPD7 segment. Fertilization between a normal spermatocyte and oocyte leads to a disomic zygote. Mitosis starts with chromosome replication, and unusual recombinations occur between a maternal and paternal chromatid. A daughter cell with partial isodisomic matUPD7 will be the result in 1/4 of the possible chromatid combinations. When one daughter cell has partial isodisomic matUPD7, the other will have partial isodisomic patUPD7. If both daughter cells survive, this will lead to mosaic UPD. However, because only the matUPD7 phenotype was observed in this patient, the patUPD7 daughter cell must have been eliminated. Loss of the patUPD7 cell may be a result of homozygosity for a lethal allele, loss of crucial chromosomal regions on the maternal chromosome, or other factors affecting the viability of the cell.