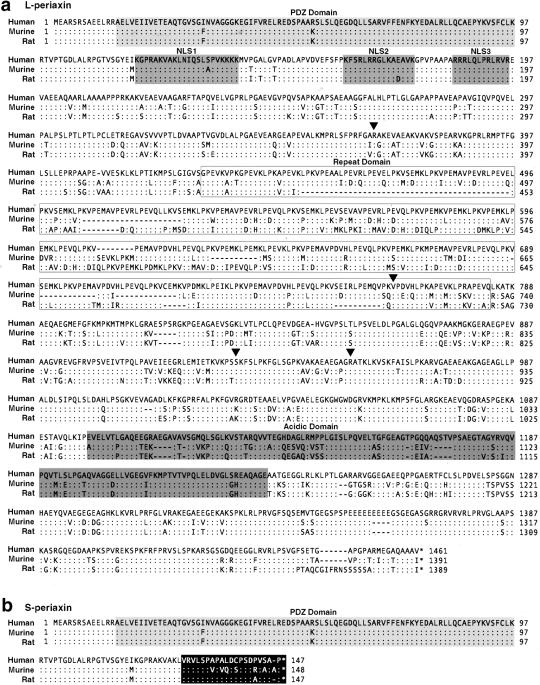
Figure 2.
Comparison of human, murine, and rat L-periaxin (a) and S-periaxin (b) amino acid sequences. a, Human L-periaxin has ∼78% and ∼73% sequence identity with the murine and rat proteins, respectively. The PDZ domain, tripartite nuclear localization signal (NLS1, NLS2, and NLS3), repeat domain, and acidic domain previously characterized in mice and rats are conserved in humans. Arrowheads indicate mutations identified in patients. b, S- and L-periaxin share a common amino terminal, but retention of intron 6 in the mRNA encoding S-periaxin results in a truncated protein with 20 amino acids encoded within the intron (blackened box). Identical amino acids are indicated by a colon (:), gaps by a dash (—) and stop codons by an asterisk (*).