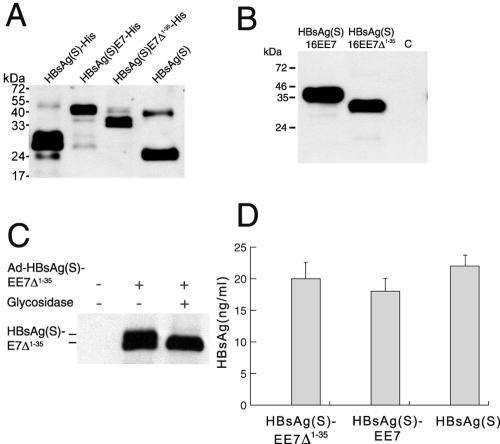
FIG. 2.
Expression and secretion of HBsAg/E7 fusion proteins. (A) Expression of HBsAg/E7 fusion proteins in yeast. Western blotting using anti-HBsAg antibodies was carried out to detect His-tagged wild-type and chimeric HBsAg(S) proteins purified from yeast on Ni-nitrilotriacetic acid agarose. A wild-type HBsAg(S) with no His tag (Engerix B) was included. Note the higher molecular mass of HBsAg(S)-His compared to the nontagged protein. (B) Western blot analysis of HEK 293T cells transfected with pIRES-neo2 plasmids encoding FLAG-tagged HBsAg(S)16E7 or HBsAg(S)16E7Δ1-35, as indicated. Cellular extracts prepared 48 h after transfection were separated in a 15% acrylamide gel and hybridized with anti-FLAG M2 monoclonal antibodies. Note the thickness of the bands due to the presence of glycosylated and nonglycosylated forms running close to each other. The apparent molecular masses are 40 and 33 kDa, respectively. C, control cells transfected with pIRES-neo2 empty vector. (C) The HBsAg(S)/E7 fusion protein is glycosylated. Western blot analysis of lysates from HEK 293T cells infected with Ad-HBsAg(S)EE7Δ1-35 before and after treatment with Endo H and detected with anti-FLAG antibodies is shown. (D) Detection of HBsAg particles in supernatants of HeLa cells transfected with plasmids encoding either HBsAg(S)16E7, HBsAg(S)16E7Δ1-35 or wild-type HBsAg(S). Transfection efficiencies were normalized by cotransfection with a plasmid expressing green fluorescent protein. At 48 h after transfection, cell supernatants were subjected to ELISA (Monolisa). A standard curve was obtained using known amounts of a commercial HBsAg(S) particle preparation (Engerix B). Data are the means ± standard deviations of three independent transfections.