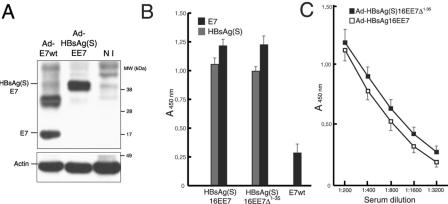
FIG. 5.
Antibody reactivity to E7 and HBsAg(S) in vaccinated mice determined by ELISA. (A) Expression of E7 and HBsAg(S)E7 in HEK 293 cells infected with either Ad-E7wt (MOI of 100) or Ad-HBsAg(S)EE7 (MOI of 10). At 48 h after infection, the cells were lysed with SDS loading buffer and equal amounts were loaded on a 4 to 20% gradient gel. After blotting, the E7 and HBsAg(S)E7 proteins were detected with anti-E7 and anti-actin antibodies. The upper band in the lane Ad-E7wt represents likely a dimer. NI, noninfected control cells. (B) Groups of BALB/c mice were inoculated at 2-week intervals with 106 IFU of either Ad-HBsAg(S)16EE7, Ad-HBsAg(S)16EE7Δ1-35 or Ad-E7wt, as indicated. Results correspond to serum samples taken 2 weeks after the third inoculation. The sera were diluted 1:200 and assayed on plates coated with either recombinant E7 or HBsAg protein as described in Materials and Methods. Data are the means ± standard deviations of 10 serum samples. (C) Extinction curves of anti-E7 antibody titers of sera derived from the mice immunized with Ad-HBsAg(S)16EE7 or Ad-HBsAg(S)16EE7Δ1-35 vectors in panel A showing slightly higher titer values for the latter and extinction values for both beyond a dilution of 1:3,200. The ELISA plates were coated with the indicated proteins as described in Materials and Methods. The results show the mean OD and the standard deviation.