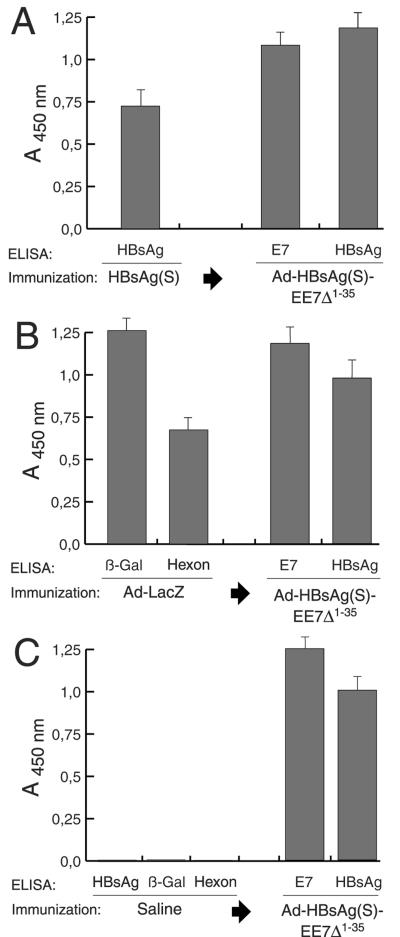
FIG. 6.
Antibody reactivity to E7 and HBsAg(S) in mice preimmunized with HBsAg or Ad-LacZ determined by ELISA. (A) BALB/c mice (n = 10) were first immunized i.m. with HBsAg(S) protein. Serum reactivity to HBsAg(S) was tested after 2 weeks after the third boost (left column). Subsequently, the mice were inoculated three times at 2-week intervals with Ad-HBsAg(S)16EE7Δ1-35. Serum samples were taken 2 weeks after the last inoculation and antibody titers against E7 and HBsAg were tested. (B) Vaccination of C57BL/6 mice (n = 10) preimmunized with Ad-LacZ. Mice were inoculated with Ad-LacZ at days 0, 14, and 28, beginning 2 weeks after the last boost antibody responses to the β-galactosidase and hexon proteins were tested. Subsequent vaccination with Ad-HBsAg(S)16EE7Δ1-35 induced additional antibody response against E7 and boosted the anti-HBsAg(S) (third and fourth columns from the left, respectively) (compare with panels A and C). (C) A control group of 10 C57BL/6 mice were injected with saline three times at 2-week intervals. Two weeks after the last injection the mice were tested for HBsAg, β-galactosidase, and Ad hexon antibodies. Then the mice were inoculated with Ad-HBsAg(S)16EE7Δ1-35 and tested as above for E7 and HBsAg antibodies. ELISA plates were coated with the indicated proteins as described in Materials and Methods. Data are the mean of 10 serum samples; the error bars represent one standard deviation from the mean values. Sera were diluted 1:200, and the cutoff value was 0.045 throughout.