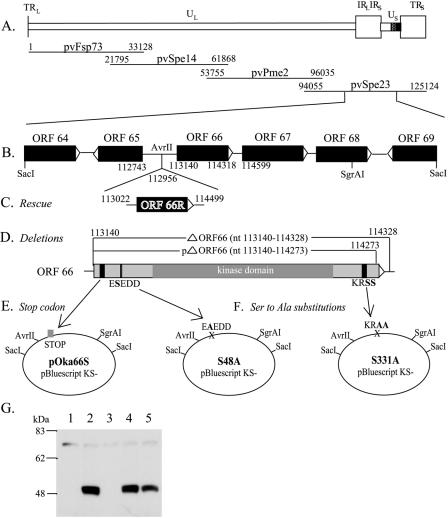
FIG. 1.
Construction of cosmid vectors with mutations in VZV pOka ORF66. (A) Schematic diagram of the VZV genome with the location of ORF66 in the Us region and the four overlapping segments of the VZV genome used to construct the VZV pOka cosmids. All coordinates given are for the pOka strain used to generate these cosmids; the equivalent coordinates for the Dumas sequence are given in Materials and Methods. (B) The 6.1-kb SacI-SacI fragment, subcloned from cosmid pvSpe23ΔAvr into pBluescript KS(−). (C) ORF66R, containing the ORF66 gene along with upstream and downstream elements, was inserted into the unique AvrII site to rescue lethal mutations. (D) Two ORF66 deletion mutants were made, removing all or most of the ORF66 sequence. (E) Four STOP codons were inserted at amino acid 21 of ORF66 to yield the ORF66S construct. (F) Two point mutations were made in putative phosphorylation sites: S48A and S331A. All mutations were reinserted into Spe23 via the 4.5-kb AvrII-SgrAI fragment. (G) Immunoblot analysis of lysate from uninfected melanoma (MeWo) cells (lane 1) or melanoma cells infected with pOka (lane 2), pOka66S (lane 3), pOka66S48A (lane 4), or pOka66S331A (lane 5). ORF66 is detected at approximately 48 kDa by ORF66-specific antibodies.