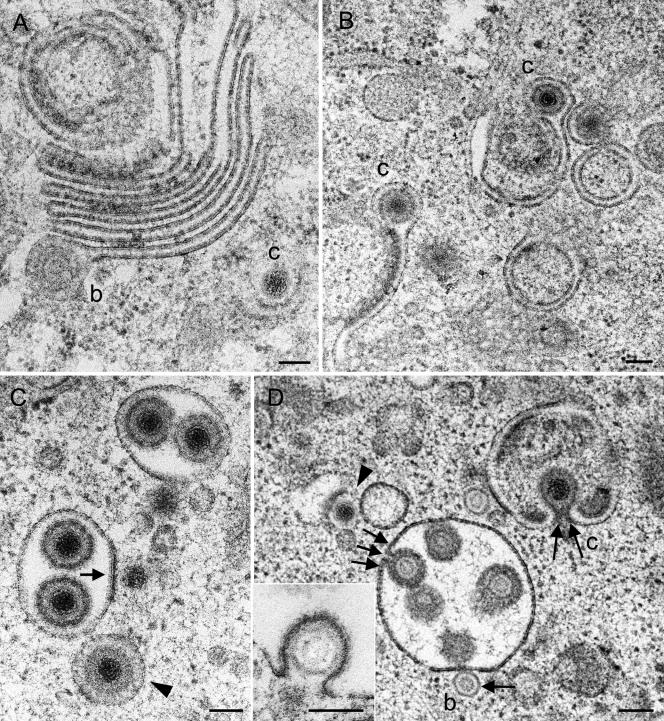
FIG. 7.
Golgi complex and packaging-derived vacuoles or cross-sectioned Golgi cisternae in Vero 2-2 cells incubated for 12 h (A, B, and C) and 15 h (D) with HSV-1. (A) Large Golgi complex bearing a virion with a B-capsid (b) at the lateral end of a Golgi cisterna in a late stage of packaging. C-capsid (c) budding is shown at a banana-shaped membrane. (B) Two single Golgi cisternae with C-capsids late in packaging. (C) Two vacuoles derived from packaging or cross-sectioned Golgi cisternae, each containing two virions, and a vacuole (arrowhead) with a virion exactly in the center, with the space between the envelope and the vacuolar membrane containing a dense substance that might have resulted from wrapping or packaging. C-capsids are in close apposition to the packaging-derived vacuoles, one of which is in an initial phase of budding (arrow). (D) B-capsid in an initial phase (arrow) and C-capsid in a late phase (two arrows) of budding into vacuoles or cross-sectioned Golgi cisternae. One virion (three arrows) is shown either immediately prior to completion of budding or in an early stage of fusion. A C-capsid (arrowhead) in an early phase of budding at a banana-shaped membrane is shown. The inset shows a B-capsid close to completion of budding into a vacuole. Bars, 100 nm.