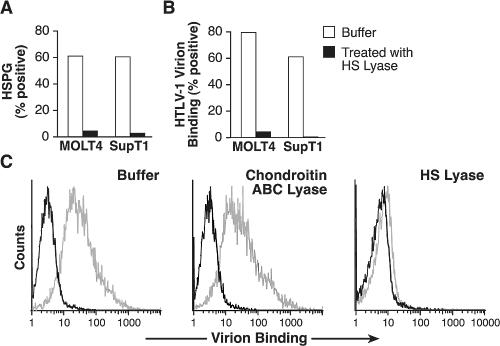
FIG. 5.
Binding of HTLV-1 virions to CD4+ T cells involves interaction with HSPGs. (A and B) SupT1 and MOLT4 cells incubated either with or without HS lyase. Some cells were assayed for the ability to bind F58-10E4, and the remainder were exposed to concentrated HTLV-1 virions, with the amount of virion binding determined as described in Materials and Methods. The percentage of cells positive for virion binding was determined by subtracting the amount of anti-SU antibody binding observed in the absence of virus from that observed in the cells exposed to the virions. (A) Binding of F58-10E4 antibody. (B) Binding of HTLV-1 virions. (C) Activated CD4+ T cells isolated from adult peripheral blood were incubated for 2 h at 37°C in either buffer alone (left) or with buffer containing 1 U of chondroitin ABC lyase (middle) or 10 mU of HS lyase (right). Cells were then exposed to HTLV-1 virions, and the amount of virion binding was determined as described for panel B. Dark lines, binding in the absence of virions; light lines, binding in the presence of virions. The data shown are from a representative experiment out of five (A and B) or three (C) performed.