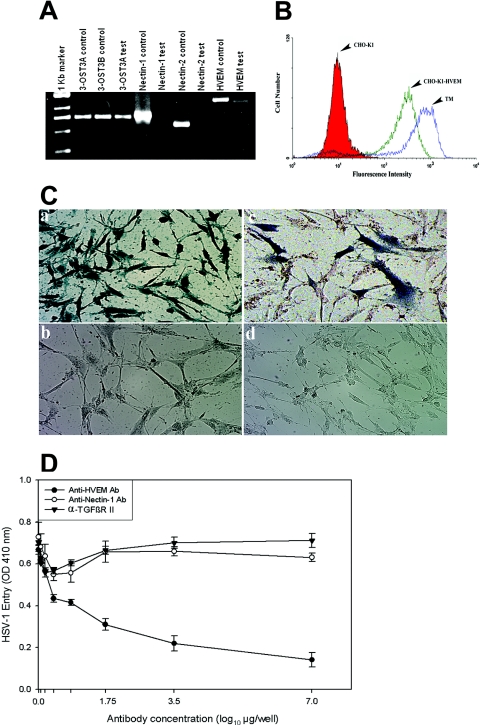
FIG. 3.
HVEM is the major mediator of entry into TM cells. (A) mRNAs specific to HVEM and 3-OST-3 but not to nectin-1 or nectin-2 were detected in TM cells. RT-PCR assays were performed. cDNAs were produced from total RNA isolated from the cells. PCR was performed using primers specific to each receptor (indicated at top). Either the expression plasmids for each receptor (indicated as controls) or cDNA isolated from TM cells (indicated as tests) were used as templates. The products were separated by electrophoresis on an agarose gel and then stained with ethidium bromide. Amplification products specific to HVEM and 3-OST-3 but not to nectin-1 or nectin-2 were detected in cDNAs generated from TM cells. (B) Cell surface expression of HVEM in TM cells detected by fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) analysis. Monolayers of cultured TM cells were incubated at 4°C for 30 min with anti-HVEM antibody (1:200 dilution). CHO-K1 cells stably expressing HVEM (CHO-K1-HVEM) and wild-type CHO-K1 cells were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. Cells were examined by FACS analysis after 30 min of incubation with secondary anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G antibody (1:500 dilution) conjugated with FITC. (C) TM cells are resistant to BHV-1 entry. Cultured human TM cells (panels a and b), TM cells transiently transfected with the nectin-1 expression plasmid pBG38 (panel c), or TM cells mock transfected with empty vector (panel d) were exposed to β-galactosidase-expressing recombinants (40 PFU/cell) of HSV-1 (panel a) and BHV-1 (panels b, c, and d). After 6 h of infection at 37°C, cells were washed three times with PBS, fixed and permeabilized, and incubated with X-Gal (Invitrogen), which yields an insoluble blue product upon hydrolysis by β-galactosidase. Microscopy was performed using a 20× objective of the inverted microscope (Axiovert 100 M; Zeiss). The slide book version 3.0 was used for images. Blue cells (representing viral entry) were seen as shown. (D) Anti-HVEM polyclonal antibody, but not anti-nectin-1 antibody, inhibits HSV-1 entry into cultured human TM. Cells plated in 96-well plates were incubated with twofold dilutions of the anti-HVEM antibody (Ab), anti-nectin-1 Ab, and a control with α-TGFβR II Ab for 1 h 30 min at room temperature. Cells were then challenged with equal doses of HSV-1 (KOS) gL86 prepared in PBS with 1% glucose and 0.1% heat-inactivated calf serum at 37°C. After 2 h 30 min, cells were washed one time with PBS and treated for a short period with citrate buffer. Finally, cells were washed three times with PBS and incubated for 4 h in PBS buffer at 37°C. The substrate, ImmunoPure ONPG (o-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside), was prepared in PBS buffer with nonionic detergent (Igepal CA-630; Sigma), and β-galactosidase activity was read at an optical density (OD) at 410 nm. The concentrations of the antibody used are expressed in μg/well. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results.