Abstract
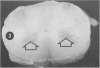
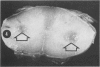
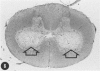
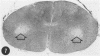
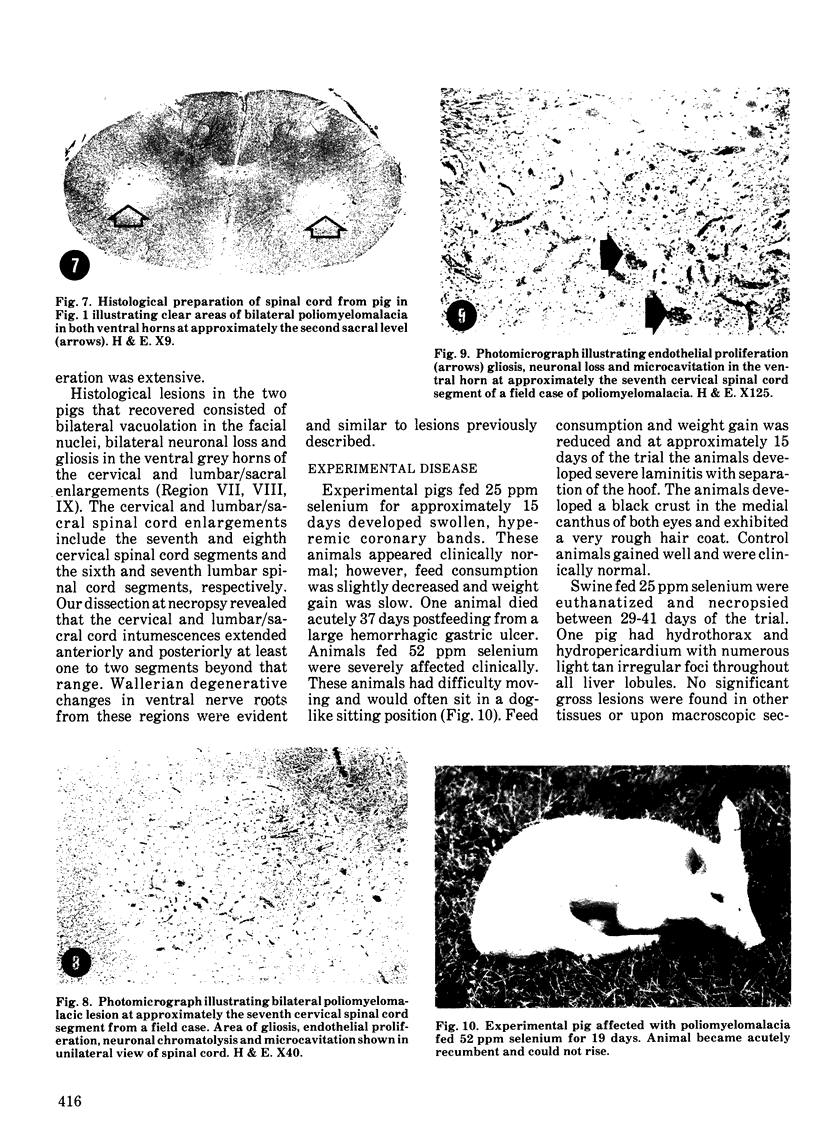
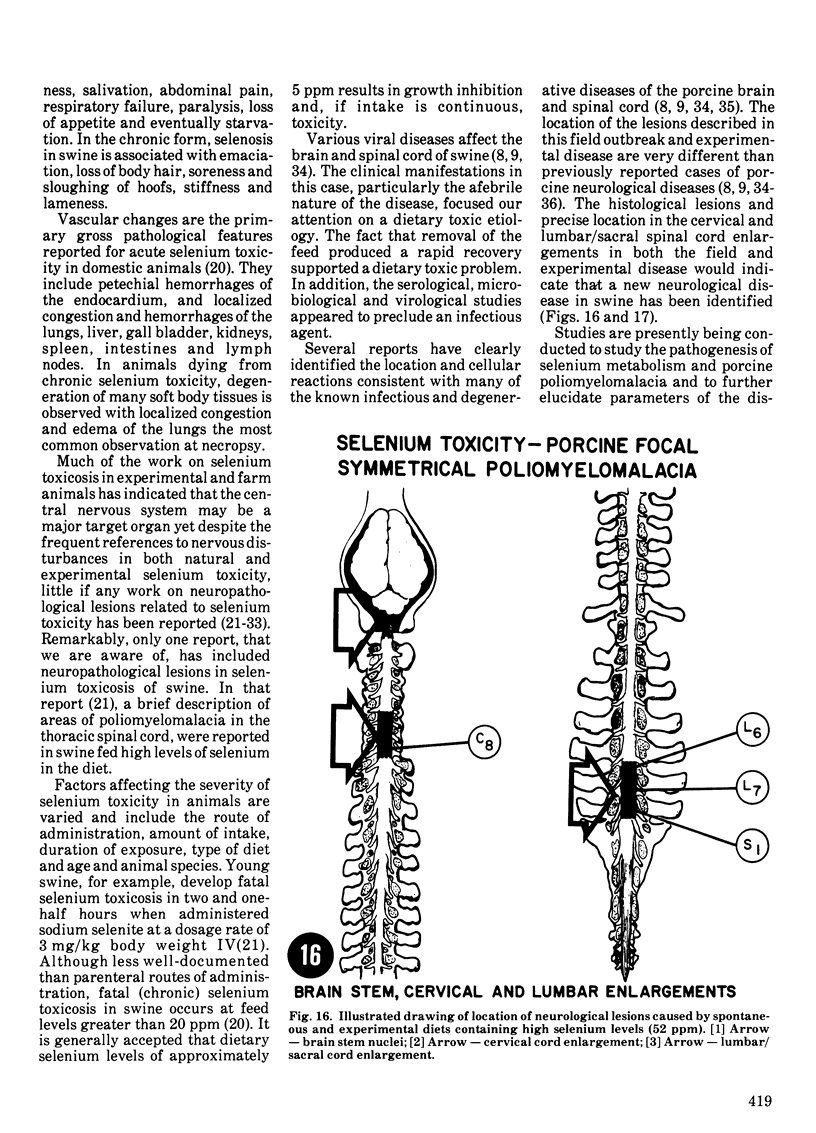
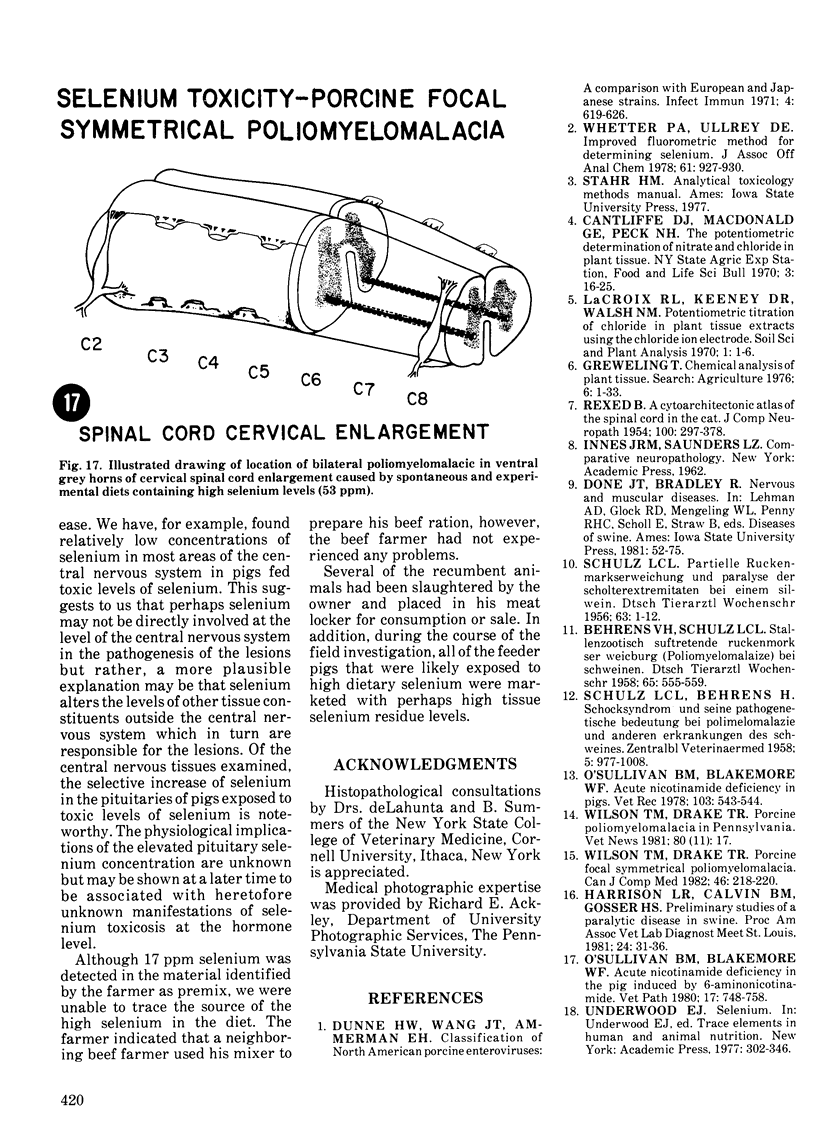
An acute afebrile paretic condition was diagnosed in 18 of 225 feeder pigs between eight to ten weeks of age. Nine pigs died acutely, seven pigs were euthanatized and two appeared to recover. Macroscopic lesions in the ventral horns of the cervical and lumbar/sacral spinal cord enlargements consisted of focal, bilateral, depressed areas. Histopathologically, the lesion consisted of endothelial proliferation, glial cell reaction and microcavitation. Similar lesions were observed in some brain stem motor nuclei. High selenium levels were detected in the pig feed and in pig tissues and blood. Two of five experimental pigs fed a commercial grower ration and supplemented with 52 ppm selenium as sodium selenite developed paresis and paralysis after a 29 day feeding trial. Histopathological lesions of focal symmetrical poliomyelomalacia confined to the cervical and lumbar/sacral spinal cord enlargements, and identical to those in the field cases, were produced. Select brain stem motor nuclei were also affected.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Diehl J. S., Mahan D. C., Moxon A. L. Effects of single intramuscular injections of selenium at various levels to young swine. J Anim Sci. 1975 May;40(5):844–850. doi: 10.2527/jas1975.405844x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diplock A. T. Metabolic aspects of selenium action and toxicity. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol. 1976 Feb;4(3):271–329. doi: 10.1080/10408447609164016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne H. W., Wang J. T., Ammerman E. H. Classification of North American porcine enteroviruses: a comparison with European and Japanese strains. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):619–631. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.619-631.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch R. C., Clark J. D., Jain A. V., Mahaffey E. A. Treatment of induced acute selenosis in rats and weanling pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Dec;40(12):1808–1811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herigstad R. R., Whitechair C. K., Olson O. E. Inorganic and organic selenium toxicosis in young swine: comparison of pathologic changes with those in seine with vitamin E-selenium deficiency. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Oct;34(10):1227–1238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkinson W. I. Syringomyelia in pigs. Aust Vet J. 1980 Oct;56(10):506–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1980.tb02569.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald D. W., Christian R. G., Strausz K. I., Roff J. Acute selenium toxicity in neonatal calves. Can Vet J. 1981 Sep;22(9):279–281. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. H., Nielsen S. W. Porcine polioencephalomyelitides. Adv Vet Sci. 1968;12:33–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan B. M., Blakemore W. F. Acute nicotinamide deficiency in pigs. Vet Rec. 1978 Dec 9;103(24):543–544. doi: 10.1136/vr.103.24.543-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan B. M., Blakemore W. F. Acute nicotinamide deficiency in the pig induced by 6-aminonicotinamide. Vet Pathol. 1980 Nov;17(6):748–758. doi: 10.1177/030098588001700610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORSTADIUS K. Toxicity of a single subcutaneous dose of sodium selenite in pigs. Nature. 1960 Dec 24;188:1117–1117. doi: 10.1038/1881117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield J. E. The selenium story: some reflections on the "moon-metal". N Z Vet J. 1974 Jun;22(6):85–94. doi: 10.1080/00480169.1974.34140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REXED B. A cytoarchitectonic atlas of the spinal cord in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1954 Apr;100(2):297–379. doi: 10.1002/cne.901000205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Vleet J. F., Meyer K. B., Olander H. J. Acute selenium toxicosis induced in baby pigs by parenteral administration of selenium-vitamin E preparations. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1974 Sep 15;165(6):543–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T. M., Drake T. R. Porcine focal symmetrical poliomyelomalacia. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Apr;46(2):218–220. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]