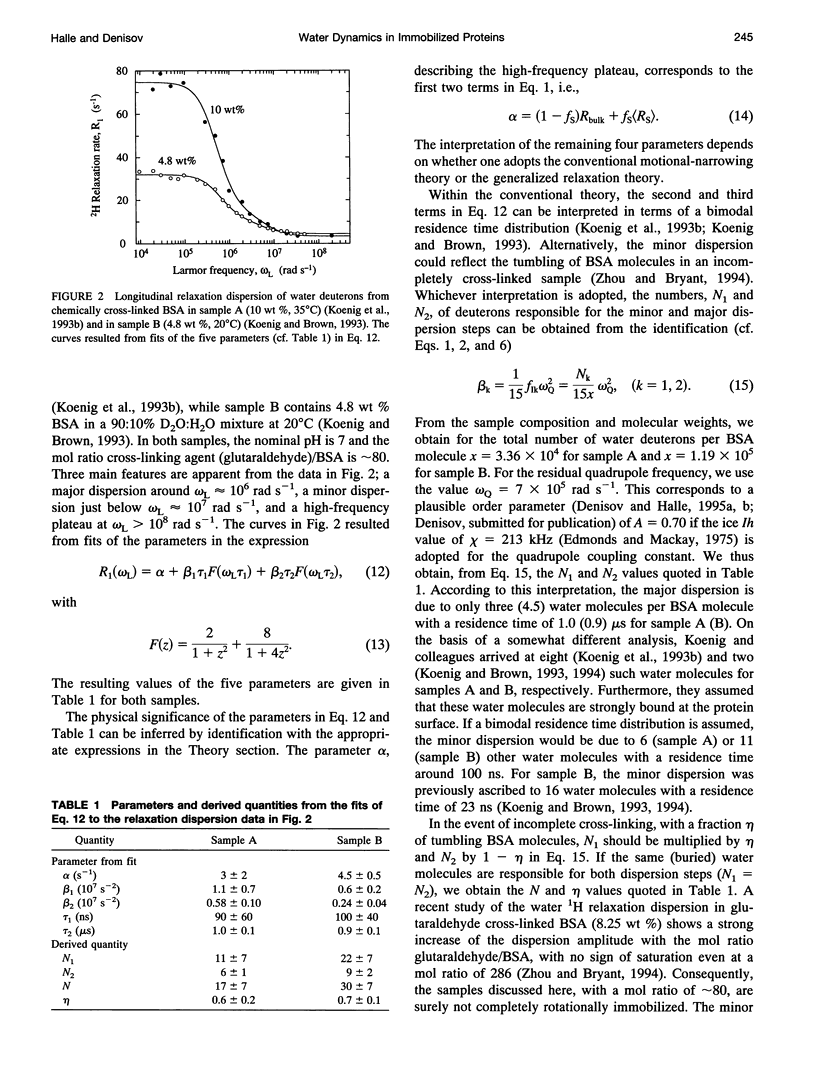
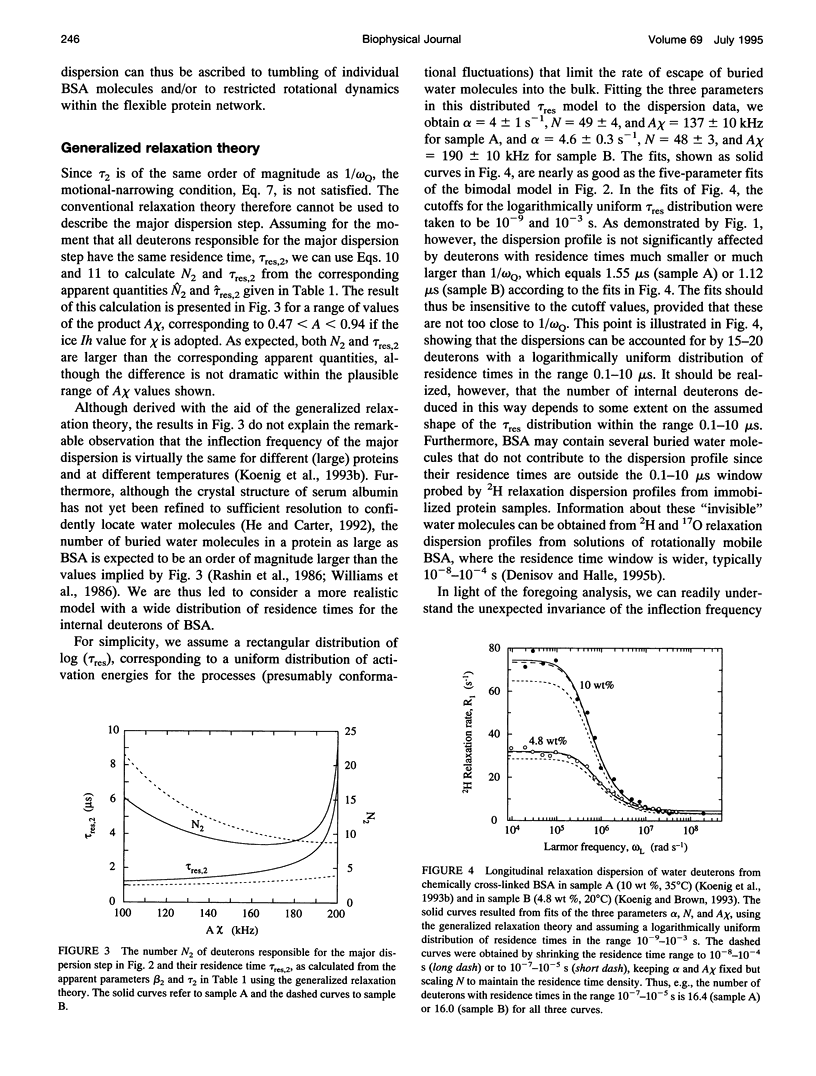
Abstract
The inflection frequency of the deuteron magnetic relaxation dispersion from water in rotationally immobilized protein samples has recently been found to be essentially independent of temperature and protein structure. This remarkable invariance has been interpreted in terms of a universal residence time of 1 microseconds for protein-associated water molecules. We demonstrate here that this interpretation is an artifact of the conventional perturbation theory of spin relaxation, which is not valid for rotationally immobile proteins. Using a newly developed non-perturbative, stochastic theory of spin relaxation, we identify the apparent correlation time of 1 microseconds with the inverse of the nuclear quadrupole frequency, thus explaining its invariance. The observed dispersion profiles are consistent with a broad distribution of residence times, spanning the microseconds range. Furthermore, we argue that the deuteron dispersion is due to buried water molecules rather than to the traditional surface hydration previously invoked, and that the contribution from rapidly exchanging protein hydrogens cannot be neglected. The conclusions of the present work are also relevant to proton relaxation in immobilized protein samples and to magnetic resonance imaging of soft tissue.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker E. N., Hubbard R. E. Hydrogen bonding in globular proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1984;44(2):97–179. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(84)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belton P. S. NMR studies of protein hydration. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1994;61(1):61–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. R. Structural origins of mammalian albumin. Fed Proc. 1976 Aug;35(10):2141–2144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. D., 3rd, Koenig S. H. 1/T1 rho and low-field 1/T1 of tissue water protons arise from magnetization transfer to macromolecular solid-state broadened lines. Magn Reson Med. 1992 Nov;28(1):145–152. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910280115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunne R. M., Liepinsh E., Otting G., Wüthrich K., van Gunsteren W. F. Hydration of proteins. A comparison of experimental residence times of water molecules solvating the bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor with theoretical model calculations. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jun 20;231(4):1040–1048. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daggett V., Levitt M. Realistic simulations of native-protein dynamics in solution and beyond. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1993;22:353–380. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.22.060193.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denisov V. P., Halle B. Hydrogen exchange and protein hydration: the deuteron spin relaxation dispersions of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor and ubiquitin. J Mol Biol. 1995 Feb 3;245(5):698–709. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denisov V. P., Halle B. Protein hydration dynamics in aqueous solution: a comparison of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor and ubiquitin by oxygen-17 spin relaxation dispersion. J Mol Biol. 1995 Feb 3;245(5):682–697. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.0055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englander S. W., Kallenbach N. R. Hydrogen exchange and structural dynamics of proteins and nucleic acids. Q Rev Biophys. 1983 Nov;16(4):521–655. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grösch L., Noack F. NMR relaxation investigation of water mobility in aqueous bovine serum albumin solutions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 26;453(1):218–232. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X. M., Carter D. C. Atomic structure and chemistry of human serum albumin. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):209–215. doi: 10.1038/358209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M. Dynamic properties of bound water studied through macroscopic water relaxations in concentrated protein solutions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Sep 21;1208(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(94)90162-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmich R., Gneiting T., Kotitschke K., Schnur G. Fluctuations, exchange processes, and water diffusion in aqueous protein systems: A study of bovine serum albumin by diverse NMR techniques. Biophys J. 1990 Nov;58(5):1183–1197. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82459-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S. H., Brown R. D., 3rd A molecular theory of relaxation and magnetization transfer: application to cross-linked BSA, a model for tissue. Magn Reson Med. 1993 Dec;30(6):685–695. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910300606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S. H., Brown R. D., 3rd, Ugolini R. A unified view of relaxation in protein solutions and tissue, including hydration and magnetization transfer. Magn Reson Med. 1993 Jan;29(1):77–83. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910290114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S. H., Hallenga K., Shporer M. Protein-water interaction studied by solvent 1H, 2H, and 17O magnetic relaxation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2667–2671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S. H., Schillinger W. E. Nuclear magnetic relaxation dispersion in protein solutions. I. Apotransferrin. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3283–3289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Liepinsh E., Wüthrich K. Protein hydration in aqueous solution. Science. 1991 Nov 15;254(5034):974–980. doi: 10.1126/science.1948083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashin A. A., Iofin M., Honig B. Internal cavities and buried waters in globular proteins. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3619–3625. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler P. J., Tucker A. pH-induced structural transitions of bovine serum albumin. Histidine pKa values and unfolding of the N-terminus during the N to F transition. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Mar 15;212(3):811–817. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer G., Kimmich R., Nusser W. Deuteron field-cycling relaxation spectroscopy and translational water diffusion in protein hydration shells. Biophys J. 1988 Mar;53(3):397–404. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83116-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanki N., Thornton J. M., Goodfellow J. M. Distributions of water around amino acid residues in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):637–657. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90292-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. A., Goodfellow J. M., Thornton J. M. Buried waters and internal cavities in monomeric proteins. Protein Sci. 1994 Aug;3(8):1224–1235. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560030808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D., Bryant R. G. Magnetization transfer, cross-relaxation, and chemical exchange in rotationally immobilized protein gels. Magn Reson Med. 1994 Dec;32(6):725–732. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910320607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


