Abstract
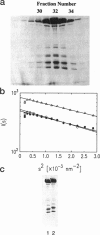
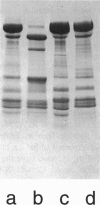
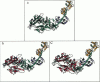
Reductive methylation of nearly all lysine groups of myosin subfragment-1 (S1) was required for crystallization and solution of its structure at atomic resolution. Possible effects of such methylation on the radius of gyration of chicken skeletal muscle myosin S1 have been investigated by using small-angle neutron scattering. In addition, we have investigated the effect of MgADP.Vi, which is thought to produce an analog of the S1.ADP.Pi state, on the S1 radius of gyration. We find that although methylation of S1, with or without SO42- ion addition, does not significantly alter the structure, addition of ADP plus vanadate does decrease the radius of gyration significantly. The S1 crystal structure predicts a radius of gyration close to that measured here by neutron scattering. These results suggest that the overall shape by crystallography resembles nucleotide-free S1 in solution. In order to estimate the effect of residues missing from the crystal structure, the structure of missing loops was estimated by secondary-structure prediction methods. Calculations using the complete crystal structure show that a simple closure of the nucleotide cleft by a rigid-body torsional rotation of residues (172-180 to 670) around an axis running along the base of the cleft alone does not produce changes as large as seen here and in x-ray scattering results. On the other hand, a rigid body rotation of either the light-chain binding domain (767 to 843 plus light chains) or of a portion of 20-kDa peptide plus this domain (706 to 843 plus light chains) is more readily capable of producing such changes.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguirre R., Gonsoulin F., Cheung H. C. Interaction of fluorescently labeled myosin subfragment 1 with nucleotides and actin. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6827–6835. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagshaw C. R., Sutcliffe M. J. Another turn for E-F hands. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Apr;1(4):209–212. doi: 10.1038/nsb0494-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. J., Smith C. A., Thoden J., Smith R., Sutoh K., Holden H. M., Rayment I. Structural studies of myosin:nucleotide complexes: a revised model for the molecular basis of muscle contraction. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):19S–28S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks-Skiba K., Cooke R. The conformation of the active site of myosin probed using mant-nucleotides. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):142S–149S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fretheim K., Iwai S., Feeney R. E. Extensive modification of protein amino groups by reductive addition of different sized substituents. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1979;14(5):451–456. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1979.tb01956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita Y., Noda Y. Effect of reductive alkylation on thermal stability of ribonuclease A and chymotrypsinogen A. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1991 Nov;38(5):445–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1991.tb01525.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrigos M., Mallam S., Vachette P., Bordas J. Structure of the myosin head in solution and the effect of light chain 2 removal. Biophys J. 1992 Dec;63(6):1462–1470. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81743-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodno C. C. Myosin active-site trapping with vanadate ion. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):116–123. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodno C. C., Taylor E. W. Inhibition of actomyosin ATPase by vanadate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Z., Gabriel J. M., Baldwin M. A., Fletterick R. J., Prusiner S. B., Cohen F. E. Proposed three-dimensional structure for the cellular prion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):7139–7143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibel K. Comparison of neutron and X-ray scattering of dilute myoglobin solutions. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 5;93(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KITAGAWA S., YOSHIMURA J., TONOMURA Y. On the active site of myosin A-adenosine triphosphatase. II. Properties of the trinitrophenyl enzyme and the enzyme free from divalent cations. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:902–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margossian S. S., Lowey S. Preparation of myosin and its subfragments from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):55–71. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means G. E. Reductive alkylation of amino groups. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:469–478. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson R. A., Bivin D., Curmi P. M., Schneider D. K., Stone D. B. Recent neutron scattering studies of muscle contraction and its control. Adv Biophys. 1991;27:143–153. doi: 10.1016/0065-227x(91)90014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhlrad A., Peyser Y. M., Ringel I. Effects of ions on vanadate-induced photocleavage of myosin subfragment 1. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Oct 15;201(2):409–415. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phan B. C., Cheung P., Miller C. J., Reisler E., Muhlrad A. Extensively methylated myosin subfragment-1: examination of local structure, interactions with nucleotides and actin, and ligand-induced conformational changes. Biochemistry. 1994 Sep 20;33(37):11286–11295. doi: 10.1021/bi00203a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Holden H. M., Whittaker M., Yohn C. B., Lorenz M., Holmes K. C., Milligan R. A. Structure of the actin-myosin complex and its implications for muscle contraction. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):58–65. doi: 10.1126/science.8316858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Rypniewski W. R., Schmidt-Bäse K., Smith R., Tomchick D. R., Benning M. M., Winkelmann D. A., Wesenberg G., Holden H. M. Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: a molecular motor. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):50–58. doi: 10.1126/science.8316857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ring C. S., Kneller D. G., Langridge R., Cohen F. E. Taxonomy and conformational analysis of loops in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1992 Apr 5;224(3):685–699. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90553-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rypniewski W. R., Holden H. M., Rayment I. Structural consequences of reductive methylation of lysine residues in hen egg white lysozyme: an X-ray analysis at 1.8-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 21;32(37):9851–9858. doi: 10.1021/bi00088a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatsky M. A., Ho H. C., Wang J. H. Stabilization of glycogen phosphorylase b by reductive alkylation with aliphatic aldehydes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 20;303(2):298–307. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90361-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Eisenberg E. A comparison of the effect of vanadate on the binding of myosin-subfragment-1.ADP to actin and on actomyosin subfragment 1 ATPase activity. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Oct 5;193(1):69–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19305.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szent-Györgyi A. G., Szentkiralyi E. M., Kendrick-Jonas J. The light chains of scallop myosin as regulatory subunits. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 25;74(2):179–203. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashi R., Muhlrad A., Botts J. Spatial relationship between a fast-reacting thiol and a reactive lysine residue of myosin subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5661–5668. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesi C., Barman T., Travers F. Sulphate is a competitive inhibitor of the binding of nucleotide to myosin. A comparison with phosphate. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 15;236(1):256–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima Y. Y., Kron S. J., McNally E. M., Niebling K. R., Toyoshima C., Spudich J. A. Myosin subfragment-1 is sufficient to move actin filaments in vitro. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):536–539. doi: 10.1038/328536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. S., Tsai Y. H., Lauzon G., Cheng S. T. Structure and activity of methylated horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):440–443. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vibert P., Cohen C. Domains, motions and regulation in the myosin head. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1988 Aug;9(4):296–305. doi: 10.1007/BF01773873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi K., Tokunaga M., Kohno I., Sugimoto Y., Hamanaka T., Takezawa Y., Wakabayashi T., Amemiya Y. Small-angle synchrotron x-ray scattering reveals distinct shape changes of the myosin head during hydrolysis of ATP. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):443–447. doi: 10.1126/science.1411537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Yount R. G. Chemical modification of myosin by active-site trapping of metal-nucleotides with thiol crosslinking reagents. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):93–116. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. D., Rayment I. Kinetic characterization of reductively methylated myosin subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 21;32(37):9859–9865. doi: 10.1021/bi00088a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. D. Special instrumentation and techniques for kinetic studies of contractile systems. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):698–708. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie X., Harrison D. H., Schlichting I., Sweet R. M., Kalabokis V. N., Szent-Györgyi A. G., Cohen C. Structure of the regulatory domain of scallop myosin at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1994 Mar 24;368(6469):306–312. doi: 10.1038/368306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]