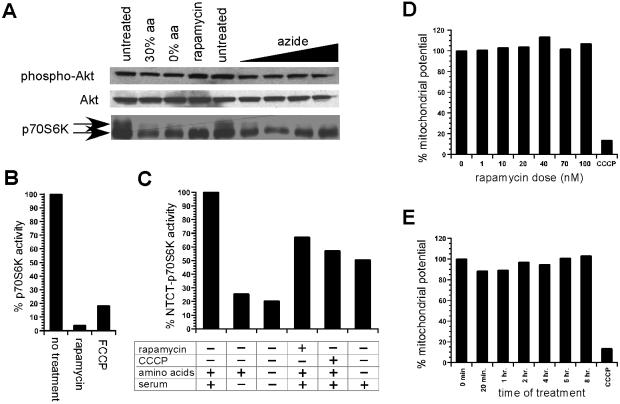
Figure 1.
Analysis of p70S6K phosphorylation in response to mitochondrial dysfunction. (A) p70S6K phospho-shift in response to untreated, 30% amino acid availability (30% aa), absence of amino acids (0% aa), rapamycin treatment, and increasing azide dosage (1 mM, 2 mM, 5 mM, 10 mM) is shown. Similar analysis of phospho-Akt and Akt is also included. (B) p70S6K activity in response to rapamycin and carbonylcyanide p-trifluoro-methoxyphenylhydrazone (FCCP) treatment. (C) Activity of ΔNTΔCT-p70S6K rapamycin-resistant allele in response to the presence of amino acids and serum, withdrawal of serum, withdrawal of amino acid and serum, rapamycin treatment, and carbonylcyanide m-chlorophenlyhydrazone (CCCP) treatment. (D) Mitochondrial activity in response to rapamycin dose is compared with CCCP-treated control measurement by using the JC-1 assay. (E) Mitochondrial activity in response to time of treatment with 50 nM rapamycin is compared with CCCP-treated control measurement.