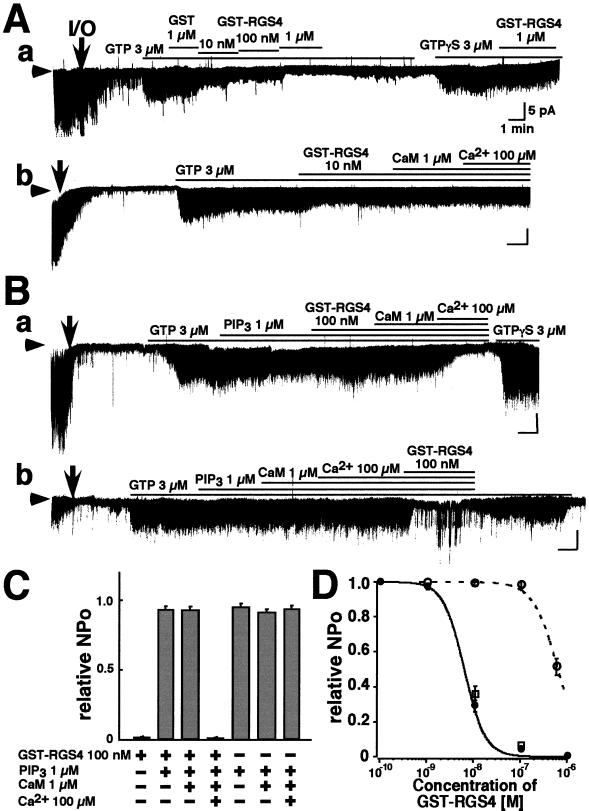
Figure 1.
The effects of RGS4, PIP3, and Ca2+/CaM upon single-channel KG currents in patches from atrial myocytes. Experiments were performed on excised inside-out membrane patches in symmetrical 150 mM K+ solutions with 0.3 μM ACh in the pipette. Arrowheads indicate the zero current level. I/O indicates the excision of the patch from the myocyte. Compounds were applied in bath solution to the internal surface of patches for the periods indicated by the bars above the current records. (A) The effects of RGS4 and Ca2+/CaM on channel activity. (a) Concentration-dependent inhibitory effect of GST-RGS4 on KG channel currents. (b) The addition of 1 μM CaM and 100 μM Ca2+ had no effect on the inhibition of KG channels by 10 nM GST-RGS4. (B) The effect of PIP3. (a) PIP3 (1 μM) severely reduced the inhibitory effect of GST-RGS4, an effect that is reversed by Ca2+/CaM. (b) In PIP3 and Ca2+/CaM the effect of GST-RGS4 was not inhibited. (C) The NPo of KG channel currents recorded under different conditions (indicated below) relative to that seen in 3 μM GTP. N represents the number of KG channels in a patch, and Po represents the open probability of each channel. Symbols and bars indicate the mean ± SEM; n = 10 for each. (D) Dose-dependent inhibition by GST-RGS4 of KG channel currents in the absence (closed circles) or presence (open circles) of 1 μM PIP3, and in the presence of 1 μM PIP3 and Ca2+/CaM (open squares). Symbols and bars indicate the mean ± SEM, n = 6 for each. Vertical bars represent 5 pA, and horizontal bars represent 1 min.