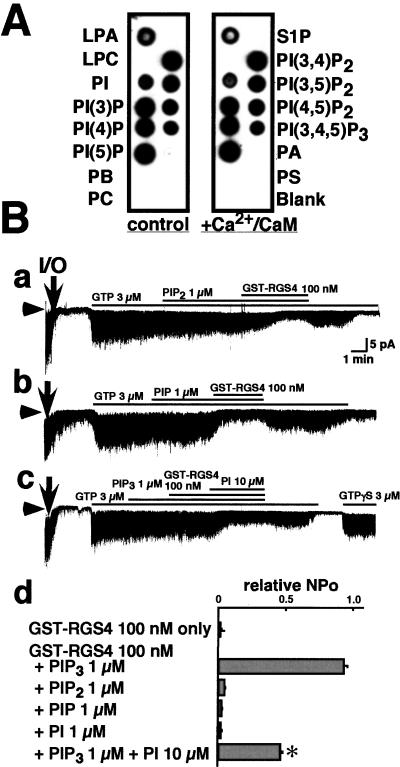
Figure 2.
Interactions between different phospholipids and RGS4. (A) Protein–lipid overlay assay of GST-RGS4. GST-RGS4 binds specifically to phosphatidylinositols and LPA (control: Left), and this binding is not affected by the addition of Ca2+/CaM (Right). The spotted phospholipids are identified on either side of the assays. LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPC, lysophosphocholine; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate; PA, phosphatidic acid; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PS, phosphatidylserine. (B) Functional specificity of the interaction between PIP3 and RGS4. Neither 1 μM PI(4,5)P2 (PIP2) (a) nor 1 μM PI(4)P (PIP) (b) block the inhibitory effect of GST-RGS4 on GTP-induced KG channel activity. PI (10 μM) competitively antagonizes the effect of 1 μM PIP3 on GST-RGS4 inhibition of KG channels (c). (d) The NPo of KG channels recorded under different conditions (indicated on the left) relative to that seen in the presence of 3 μM GTP alone. Bars indicate the mean ± SEM, n = 5 for each. ✻, P < 0.05.