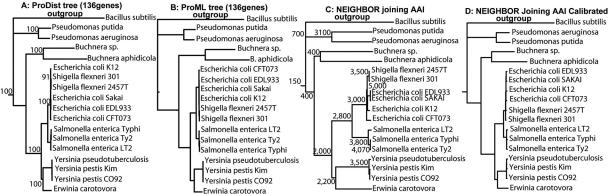
FIG. 2.
Phylogenetic reconstruction based on AAI versus whole-genome sequence analysis. The shared gene core between the 17 proteobacteria and Bacillus subtilis (outgroup) was determined, using a two-way BLAST approach, to be 136 genes, and these core genes were used to build the phylogenetic trees shown. (A and B) A distance and a maximum likelihood tree, respectively, built with the ProtDist and ProML algorithms of the Phylip package (13) using default settings and, as input sequence, the concatenated protein sequences of all 136 core genes aligned with the ClustalW software (6). The numbers on the nodes of the distance tree (A) indicate the statistical support of the node by 100 bootstrap replicates with ProtDist. All nodes (even the ones not shown for simplicity) have 100 bootstrap values, except for the node connecting strain K-12 to the two Shigella strains, which has 91. (C) The AAI-based tree. The numbers on the nodes of the AAI tree are rough approximations of the number of genes shared (and used in the calculations of AAI) by the genomes grouped at the node. The exact number of genes depends on the specific pair of genomes used. (D) The AAI tree calibrated as described in Materials and Methods.